Mindin serves as a tumour suppressor gene during colon cancer progression through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway in mice
- PMID: 32614521
- PMCID: PMC7412704
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15332
Mindin serves as a tumour suppressor gene during colon cancer progression through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway in mice
Abstract
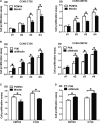
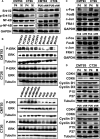
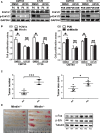
Mindin is important in broad spectrum of immune responses. On the other hand, we previously reported that mindin attenuated human colon cancer development by blocking angiogenesis through Egr-1-mediated regulation. However, the mice original mindin directly suppressed the syngenic colorectal cancer (CRC) growth in our recent study and we aimed to further define the role of mindin during CRC development in mice. We established the mouse syngeneic CRC CMT93 and CT26 WT cell lines with stable mindin knock-down or overexpression. These cells were also subcutaneously injected into C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice as well as established a colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC) mouse model treated with lentiviral-based overexpression and knocked-down of mindin. Furthermore, we generated mindin knockout mice using a CRISPR-Cas9 system with CAC model. Our data showed that overexpression of mindin suppressed cell proliferation in both of CMT93 and CT26 WT colon cancer cell lines, while the silencing of mindin promoted in vitro cell proliferation via the ERK and c-Fos pathways and cell cycle control. Moreover, the overexpression of mindin significantly suppressed in vivo tumour growth in both the subcutaneous transplantation and the AOM/DSS-induced CAC models. Consistently, the silencing of mindin reversed these in vivo observations. Expectedly, the tumour growth was promoted in the CAC model on mindin-deficient mice. Thus, mindin plays a direct tumour suppressive function during colon cancer progression and suggesting that mindin might be exploited as a therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: MAPK/ERK; colorectal cancer; mindin.
© 2020 Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Xiamen University, China. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The extracellular matrix protein mindin attenuates colon cancer progression by blocking angiogenesis via Egr-1-mediated regulation.Oncogene. 2018 Feb 1;37(5):601-615. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.359. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28991232
-
Mindin is upregulated during colitis and may activate NF-kappaB in a TLR-9 mediated manner.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Mar 7;16(9):1070-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1070. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20205276 Free PMC article.
-
The secreted matrix protein mindin increases prostate tumor progression and tumor-bone crosstalk via ERK 1/2 regulation.Carcinogenesis. 2019 Jul 20;40(7):828-839. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz105. Carcinogenesis. 2019. PMID: 31168562
-
RIP3 promotes colitis-associated colorectal cancer by controlling tumor cell proliferation and CXCL1-induced immune suppression.Theranostics. 2019 Jun 2;9(12):3659-3673. doi: 10.7150/thno.32126. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31281505 Free PMC article.
-
PIAS3-mediated feedback loops promote chronic colitis-associated malignant transformation.Theranostics. 2018 Apr 30;8(11):3022-3037. doi: 10.7150/thno.23046. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29896300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics analysis and identification of upregulated tumor suppressor genes associated with suppressing colon cancer progression by curcumin treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 5;14:1218046. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1218046. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37731740 Free PMC article.
-
Mindin orchestrates the macrophage-mediated resolution of liver fibrosis in mice.Hepatol Int. 2025 Apr 5. doi: 10.1007/s12072-025-10813-7. Online ahead of print. Hepatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40186763
-
Application of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology in basic research, diagnosis and treatment of colon cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 20;14:1148412. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1148412. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37020597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological functions and related signaling pathways of SPON2.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;13:1323744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1323744. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38264743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43‐66. - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson B. Simultaneous surgery for primary colorectal cancer and metastatic lesions? Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;47(3):269‐276. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non‐coding RNA. Human Mol Genet. 2006;15(suppl_1):R17‐R29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

