Elderly people and responses to COVID-19 in 27 Countries
- PMID: 32614889
- PMCID: PMC7332014
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235590
Elderly people and responses to COVID-19 in 27 Countries
Abstract
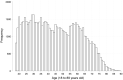
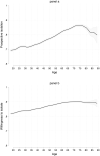
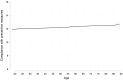
Amongst the most robust consensus related to the COVID-19 disease is that the elderly are by far the most vulnerable population group. Hence, public authorities target older people in order to convince them to comply with preventive measures. However, we still know little about older people's attitudes and compliance toward these measures. In this research, I aim to improve our understanding of elderly people's responses to the pandemic using data from 27 countries. Results are surprising and quite troubling. Elderly people's response is substantially similar to their fellow citizens in their 50's and 60's. This research (i) provides the first thorough description of the most vulnerable population's attitudes and compliance in a comparative perspective (ii) suggest that governments' strategies toward elderly people are far from successful and (iii) shows that methodologically, we should be more cautious in treating age as having a linear effect on COVID-19 related outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
YouGov provided the datasets pro bono to Imperial College London and the Institute of Global Health Innovation. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Utych S. M., & Fowler L. (2020). Age-based messaging strategies for communication about COVID-19. Journal of Behavioral Public Administration, 3(1). 10.30636/jbpa.31.151 - DOI
-
- Schneeberg A., Bettinger J. A., McNeil S., Ward B. J., Dionne M., Cooper C., et al. (2014). Knowledge, attitudes, beliefs and behaviours of older adults about pneumococcal immunization, a Public Health Agency of Canada/Canadian Institutes of Health Research Influenza Research Network (PCIRN) investigation. BMC Public Health, 14(1), 442. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

