Microglial Remodeling of the Extracellular Matrix Promotes Synapse Plasticity
- PMID: 32615087
- PMCID: PMC7497728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.050
Microglial Remodeling of the Extracellular Matrix Promotes Synapse Plasticity
Abstract
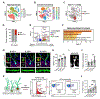
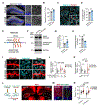
Synapse remodeling is essential to encode experiences into neuronal circuits. Here, we define a molecular interaction between neurons and microglia that drives experience-dependent synapse remodeling in the hippocampus. We find that the cytokine interleukin-33 (IL-33) is expressed by adult hippocampal neurons in an experience-dependent manner and defines a neuronal subset primed for synaptic plasticity. Loss of neuronal IL-33 or the microglial IL-33 receptor leads to impaired spine plasticity, reduced newborn neuron integration, and diminished precision of remote fear memories. Memory precision and neuronal IL-33 are decreased in aged mice, and IL-33 gain of function mitigates age-related decreases in spine plasticity. We find that neuronal IL-33 instructs microglial engulfment of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and that its loss leads to impaired ECM engulfment and a concomitant accumulation of ECM proteins in contact with synapses. These data define a cellular mechanism through which microglia regulate experience-dependent synapse remodeling and promote memory consolidation.
Keywords: microglia, hippocampus, extracellular matrix, aging, memory, dendrite remodeling, interleukin-33.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Creating Space for Synaptic Formation-A New Role for Microglia in Synaptic Plasticity.Cell. 2020 Jul 23;182(2):265-267. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.042. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32707091
-
Remodelling the matrix.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Sep;21(9):449. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0356-5. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32733063 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-33 ameliorates perioperative neurocognitive disorders by modulating microglial state.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Aug 1;253:109982. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109982. Epub 2024 May 1. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38701943
-
Astrocyte-derived interleukin-33 promotes microglial synapse engulfment and neural circuit development.Science. 2018 Mar 16;359(6381):1269-1273. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3589. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Science. 2018. PMID: 29420261 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal TIMP2 regulates hippocampus-dependent plasticity and extracellular matrix complexity.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Sep;28(9):3943-3954. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02296-5. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37914840 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33/ST2 Signaling Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Homeostasis in the Adult Hippocampal Circuitry.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Sep;40(9):1125-1130. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0491. Epub 2021 Jul 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34297618 Review.
-
Immune dysregulation and cognitive vulnerability in the aging brain: Interactions of microglia, IL-1β, BDNF and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Sep;96(Pt A):11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.020. Epub 2014 Dec 27. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25549562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Extracellular Perspective on CNS Maturation: Perineuronal Nets and the Control of Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2434. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052434. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia in brain aging: An overview of recent basic science and clinical research developments.J Biomed Res. 2024 Feb 26;38(2):122-136. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20220220. J Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 38403286 Free PMC article.
-
The Participation of Microglia in Neurogenesis: A Review.Brain Sci. 2021 May 18;11(5):658. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050658. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clec7a Worsens Long-Term Outcomes after Ischemic Stroke by Aggravating Microglia-Mediated Synapse Elimination.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(36):e2403064. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403064. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39088351 Free PMC article.
-
MAVS signaling shapes microglia responses to neurotropic virus infection.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Oct 18;21(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03258-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39425188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez DD, Giacomini D, Yang SM, Trinchero MF, Temprana SG, Büttner KA, Beltramone N, and Schinder AF (2016). A disynaptic feed-back network activated by experience promotes the integration of new granule cells. Science 354, 459–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

