Primary exposure to SARS-CoV-2 protects against reinfection in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 32616673
- PMCID: PMC7402625
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abc5343
Primary exposure to SARS-CoV-2 protects against reinfection in rhesus macaques
Abstract
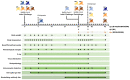
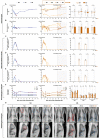
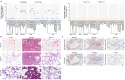
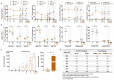
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has become a global pandemic. It is unclear whether convalescing patients have a risk of reinfection. We generated a rhesus macaque model of SARS-CoV-2 infection that was characterized by interstitial pneumonia and systemic viral dissemination mainly in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Rhesus macaques reinfected with the identical SARS-CoV-2 strain during the early recovery phase of the initial SARS-CoV-2 infection did not show detectable viral dissemination, clinical manifestations of viral disease, or histopathological changes. Comparing the humoral and cellular immunity between primary infection and rechallenge revealed notably enhanced neutralizing antibody and immune responses. Our results suggest that primary SARS-CoV-2 exposure protects against subsequent reinfection in rhesus macaques.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
Comment in
-
Can COVID-19 strike twice?Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020 Sep;18(9):477. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0424-x. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32690876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G. F., Tan W.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team , A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report,” WHO. (2020). https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
-
- Zhou L., Liu K., Liu H. G., [Cause analysis and treatment strategies of “recurrence” with novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) patients after discharge from hospital]. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 43, 281–284 (2020). - PubMed
-
- J. An et al., Clinical characteristics of the recovered COVID-19 patients with re-detectable positive RNA test. medRxiv 2020.03.26.20044222 [Preprint]. 30 March 2020. . 10.1101/2020.03.26.20044222 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

