Detection of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Based on Brain-Computer Interface
- PMID: 32617117
- PMCID: PMC7312740
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4930972
Detection of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Based on Brain-Computer Interface
Abstract
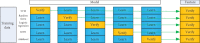
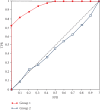
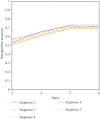
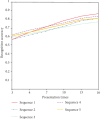
Solitary pulmonary nodules are the main manifestation of pulmonary lesions. Doctors often make diagnosis by observing the lung CT images. In order to further study the brain response structure and construct a brain-computer interface, we propose an isolated pulmonary nodule detection model based on a brain-computer interface. First, a single channel time-frequency feature extraction model is constructed based on the analysis of EEG data. Second, a multilayer fusion model is proposed to establish the brain-computer interface by connecting the brain electrical signal with a computer. Finally, according to image presentation, a three-frame image presentation method with different window widths and window positions is proposed to effectively detect the solitary pulmonary nodules.
Copyright © 2020 Shi Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




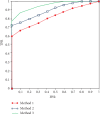
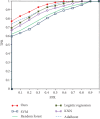
References
-
- Qiu S., Guo Q., Zhou D., Jin Y., Zhou T., He Z.'. Isolated pulmonary nodules characteristics detection based on CT images. IEEE Access. 2019;7:165597–165606. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951762. - DOI
-
- Tan D., Nijholt A. Brain-computer interfaces and human-computer interaction. In: Tan D., Nijholt A., editors. Brain-Computer Interfaces. London: Springer; 2010. pp. 3–19. (Human-Computer Interaction Series). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

