Mitochondrial Substrate Utilization Regulates Cardiomyocyte Cell Cycle Progression
- PMID: 32617517
- PMCID: PMC7331943
Mitochondrial Substrate Utilization Regulates Cardiomyocyte Cell Cycle Progression
Abstract
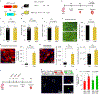
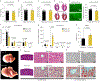
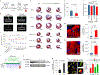
The neonatal mammalian heart is capable of regeneration for a brief window of time after birth. However, this regenerative capacity is lost within the first week of life, which coincides with a postnatal shift from anaerobic glycolysis to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, particularly towards fatty-acid utilization. Despite the energy advantage of fatty-acid beta-oxidation, cardiac mitochondria produce elevated rates of reactive oxygen species when utilizing fatty acids, which is thought to play a role in cardiomyocyte cell-cycle arrest through induction of DNA damage and activation of DNA-damage response (DDR) pathway. Here we show that inhibiting fatty-acid utilization promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation in the postnatatal heart. First, neonatal mice fed fatty-acid deficient milk showed prolongation of the postnatal cardiomyocyte proliferative window, however cell cycle arrest eventually ensued. Next, we generated a tamoxifen-inducible cardiomyocyte-specific, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) knockout mouse model to selectively enhance oxidation of glycolytically derived pyruvate in cardiomyocytes. Conditional PDK4 deletion resulted in an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and consequently an increase in glucose relative to fatty-acid oxidation. Loss of PDK4 also resulted in decreased cardiomyocyte size, decreased DNA damage and expression of DDR markers and an increase in cardiomyocyte proliferation. Following myocardial infarction, inducible deletion of PDK4 improved left ventricular function and decreased remodelling. Collectively, inhibition of fatty-acid utilization in cardiomyocytes promotes proliferation, and may be a viable target for cardiac regenerative therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests None of the authors have competing interests
Figures

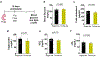
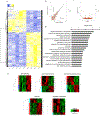
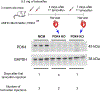
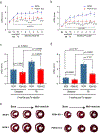

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 GM137991/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126012/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG050911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131778/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL125247/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053341/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103447/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034557/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL115275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015908/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL034557/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138983/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
