"Rigid" structure is a key determinant for the low digestibility of myoglobin
- PMID: 32617526
- PMCID: PMC7322683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2020.100094
"Rigid" structure is a key determinant for the low digestibility of myoglobin
Abstract
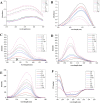
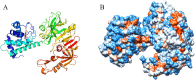
Myoglobin, a critical protein responsible for meat color, has been shown insusceptible to digestion. The underlying mechanism is not clear. The present study aimed to evaluate whether the structural properties of myoglobin are associated with its insusceptibility to digestion using spectroscopic and computational techniques. Myoglobin was degraded by only 7.03% by pepsin and 33.00% by pancreatin. The structure of myoglobin still maintained α-helix after the two-step digestion, with the exposure of some aromatic residues. In addition, molecular dynamics modeling suggested that hydrophobic amino acid residues (Phe 111, Leu 10, Ala 115, Pro 116) in pepsin and polar amino acid residues (Tyr 146, Thr 95) in myoglobin were found in the proximity of binding sites, which could result in the low digestibility of myoglobin. Our findings provide a new insight into the underlying mechanisms on the difficulty in digestion of myoglobin.
Keywords: Digestibility; Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics; Myoglobin.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the underlying mechanisms on NaCl-induced reduction in digestibility of myoglobin.Food Chem. 2022 Jun 30;380:132183. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132183. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35077987
-
Changes in the structure and digestibility of myoglobin treated with sodium chloride.Food Chem. 2021 Nov 30;363:130284. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130284. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34120050
-
The effects of high pressure treatment on the structural and digestive properties of myoglobin.Food Res Int. 2022 Jun;156:111193. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111193. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35651048
-
Glutaredoxin from rabbit bone marrow. Purification, characterization, and amino acid sequence determined by tandem mass spectrometry.J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20438-47. J Biol Chem. 1989. PMID: 2684977
-
Partial amino acid sequence of human plasma retinol-binding protein. Isolation and alignment of the five cyanogen bromide fragments and the amino acid sequences of four of the fragments.J Lipid Res. 1979 Sep;20(7):865-78. J Lipid Res. 1979. PMID: 573775
Cited by
-
Comparative Study on Hydrolysis, Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties in Simulated Digestion System between Cooked Pork and Fish Meat.Foods. 2023 Apr 23;12(9):1757. doi: 10.3390/foods12091757. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37174296 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of the mutagenic DNA lesion 1,N2-ethenoguanine induced by heated cooking oil and identification of causative agents.Genes Environ. 2023 Oct 25;45(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s41021-023-00284-3. Genes Environ. 2023. PMID: 37880746 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Freezing, Frozen Storage and Thawing on the Water Status, Quality, Nutrition and Digestibility of Meat: A Review.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 7;13(8):e70774. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70774. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40786821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Plausible Mechanism for Gastric and Colorectal Carcinogenesis: Free Radical-Mediated Acetaldehyde Generation in a Heme/Myoglobin-Linoleate-Ethanol Mixture.ACS Omega. 2021 Apr 28;6(18):12014-12021. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00614. eCollection 2021 May 11. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34056355 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-assisted immersion freezing improves the digestion properties of beef myofibrillar protein.Food Chem X. 2024 Dec 30;25:102144. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.102144. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39850056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dannenberg J.J. An introduction to hydrogen bonding by George A Jeffrey. Journal of America Chemistry Society. 1998;120(22):5604. doi: 10.1021/ja9756331. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

