Real-Time Monitoring of a Protein Biomarker
- PMID: 32619092
- PMCID: PMC8088336
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01085
Real-Time Monitoring of a Protein Biomarker
Abstract
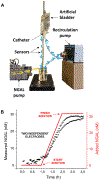
The ability to monitor protein biomarkers continuously and in real-time would significantly advance the precision of medicine. Current protein-detection techniques, however, including ELISA and lateral flow assays, provide only time-delayed, single-time-point measurements, limiting their ability to guide prompt responses to rapidly evolving, life-threatening conditions. In response, here we present an electrochemical aptamer-based sensor (EAB) that supports high-frequency, real-time biomarker measurements. Specifically, we have developed an electrochemical, aptamer-based (EAB) sensor against Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL), a protein that, if present in urine at levels above a threshold value, is indicative of acute renal/kidney injury (AKI). When deployed inside a urinary catheter, the resulting reagentless, wash-free sensor supports real-time, high-frequency monitoring of clinically relevant NGAL concentrations over the course of hours. By providing an "early warning system", the ability to measure levels of diagnostically relevant proteins such as NGAL in real-time could fundamentally change how we detect, monitor, and treat many important diseases.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; aptamer; electrochemical sensor; neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; real-time protein monitoring.
Figures


References
-
- ten Kate CA; Tibboel D; Kraemer US B-Type Natriuretic Peptide as a Parameter for Pulmonary Hypertension in Children. A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Pediatr 2015, 174 (10), 1267–1275. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA; Therneau TM; Rajkumar SV; Offord JR; Larson DR; Plevak MF; Melton LJ A Long-Term Study of Prognosis in Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance. N. Engl. J. Med 2002, 346 (8), 564–569. - PubMed
-
- Kim D-H; Cho I-H; Park J-N; Paek S-H; Cho H-M; Paek S-H Semi-Continuous, Real-Time Monitoring of Protein Biomarker Using a Recyclable Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2017, 88, 232–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

