Systematic Literature Review of Residual Symptoms and an Unmet Need in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 32619340
- PMCID: PMC8596735
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.24369
Systematic Literature Review of Residual Symptoms and an Unmet Need in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the nature and burden of residual disease in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who meet treatment targets. Second, for those who did not meet targets, to evaluate how much is due to patient symptoms.
Methods: Prospective and retrospective studies were searched in Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library in the English language from January 1, 2008 to April 18, 2018; conference abstracts (from January 2016 to April 2018) and reference lists of relevant studies were also screened.
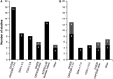
Results: Of 8,339 records identified, 55 were included in the review; 53 were unique studies, including 10 randomized controlled trials. Of these, 48 reported on patients who achieved low disease activity (LDA) or remission. Studies varied in population, treatment goals, and outcome reporting. The proportions of patients with residual symptoms in these studies varied by the definitions used for LDA or remission and were more often reported in patients with LDA than those in remission. The most commonly reported outcome measures were functional disability (n = 34 studies), tender or swollen joints (n = 18), pain (n = 17), patient global assessment (n = 15), and fatigue (n = 14). However, few studies reported the percentage of patients achieving a specific threshold, which could then be used to easily define the presence of residual symptoms.
Conclusion: Residual symptoms are present in some patients despite their achieving LDA or remission, highlighting an unmet need, especially with respect to improving pain, fatigue, and function. Standardized reporting in future observational studies would facilitate better understanding of this issue in defined RA populations.
© 2020 Eli Lilly and Company. Arthritis Care & Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:960–77. - PubMed
-
- Combe B, Logeart I, Belkacemi MC, Dadoun S, Schaeverbeke T, Daures JP, et al. Comparison of the long‐term outcome for patients with rheumatoid arthritis with persistent moderate disease activity or disease remission during the first year after diagnosis: data from the ESPOIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:724–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

