Salmonella-based platform for efficient delivery of functional binding proteins to the cytosol
- PMID: 32620833
- PMCID: PMC7335062
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-1072-4
Salmonella-based platform for efficient delivery of functional binding proteins to the cytosol
Abstract
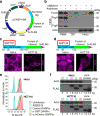
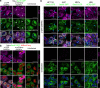
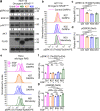
Protein-based affinity reagents (like antibodies or alternative binding scaffolds) offer wide-ranging applications for basic research and therapeutic approaches. However, whereas small chemical molecules efficiently reach intracellular targets, the delivery of macromolecules into the cytosol of cells remains a major challenge; thus cytosolic applications of protein-based reagents are rather limited. Some pathogenic bacteria have evolved a conserved type III secretion system (T3SS) which allows the delivery of effector proteins into eukaryotic cells. Here, we enhance the T3SS of an avirulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium to reproducibly deliver multiple classes of recombinant proteins into eukaryotic cells. The efficacy of the system is probed with both DARPins and monobodies to functionally inhibit the paradigmatic and largely undruggable RAS signaling pathway. Thus, we develop a bacterial secretion system for potent cytosolic delivery of therapeutic macromolecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Vivès E, Brodin P, Lebleu B. A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:16010–16017. - PubMed
-
- Derossi D, Joliot AH, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A. The third helix of the antennapedia homeodornain translocates through biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;296:10444–10450. - PubMed
-
- Smith SA, Selby LI, Johnston APR, Such GK. The endosomal escape of nanoparticles: toward more efficient cellular delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019;30:263–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

