Assessment of polygenic architecture and risk prediction based on common variants across fourteen cancers
- PMID: 32620889
- PMCID: PMC7335068
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16483-3
Assessment of polygenic architecture and risk prediction based on common variants across fourteen cancers
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have led to the identification of hundreds of susceptibility loci across cancers, but the impact of further studies remains uncertain. Here we analyse summary-level data from GWAS of European ancestry across fourteen cancer sites to estimate the number of common susceptibility variants (polygenicity) and underlying effect-size distribution. All cancers show a high degree of polygenicity, involving at a minimum of thousands of loci. We project that sample sizes required to explain 80% of GWAS heritability vary from 60,000 cases for testicular to over 1,000,000 cases for lung cancer. The maximum relative risk achievable for subjects at the 99th risk percentile of underlying polygenic risk scores (PRS), compared to average risk, ranges from 12 for testicular to 2.5 for ovarian cancer. We show that PRS have potential for risk stratification for cancers of breast, colon and prostate, but less so for others because of modest heritability and lower incidence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
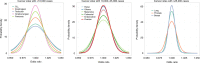
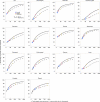
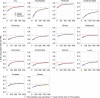
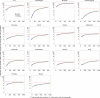
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA197350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA206110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA057726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10589/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- U01 CA167462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010480/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 19167/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

