Development of fluorescence oligonucleotide probes based on cytosine- and guanine-rich sequences
- PMID: 32620895
- PMCID: PMC7335195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-67745-5
Development of fluorescence oligonucleotide probes based on cytosine- and guanine-rich sequences
Abstract
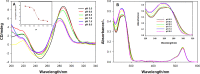
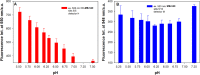
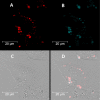
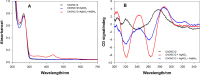
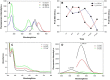
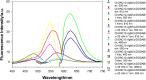
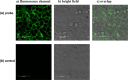
The properties of cytosine- and guanine-rich oligonucleotides contributed to employing them as sensing elements in various biosensors. In this paper, we report our current development of fluorescence oligonucleotide probes based on i-motif or G-quadruplex forming oligonucleotides for cellular measurements or bioimaging applications. Additionally, we also focus on the spectral properties of the new fluorescent silver nanoclusters based system (ChONC12-AgNCs) that is able to anchor at the Langmuir monolayer interface, which is mimicking the surface of living cells membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sen D, Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its applications for meiosi. Nature. 1998;334:364–366. - PubMed
-
- Sundquist WI, Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989;342:825–829. - PubMed
-
- Gehring K, Leroy J-L, Guéron M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine-cytosine base pairs. Nature. 1993;363:561–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

