Sulforaphane alter the microbiota and mitigate colitis severity on mice ulcerative colitis induced by DSS
- PMID: 32621086
- PMCID: PMC7334330
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-020-01053-z
Sulforaphane alter the microbiota and mitigate colitis severity on mice ulcerative colitis induced by DSS
Abstract
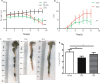
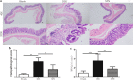
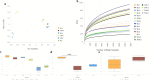
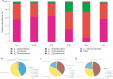
Sulforaphane (SFN) is a kind of natural isothiocyanate, which exists in cruciferous plants. Only few studies were about the anti-inflammatory effects of sulforaphane in ulcerative colitis. In this study, our purpose is to explore the effects of sulforaphane on the intestinal microbial community of UC mice. The severity of mice colitis were measured by colon length, survial rate, body weight and disease activity index (DAI) score. Histological and morphological evaluation of colon tissues were performed by HE. 16S rRNA gene amplicon pyrosequencing was used to analyza the changes of mouse flora. The variety of flora expression were explored using quantitative PCR. Sulforaphane treated mice had larger body weight and longer colon length than DSS-induced mice. The colon tissues of DSS group showed congestion and edema. Meanwhile, treatment with sulforaphane effectively reducted the damage scores and MPO activity. Sulforaphane reversed DSS-induced gut dysbiosis. Sulforaphane would shift the balance to Butyricicoccus on inflammation. The possible anti-inflammatory mechanism of sulforaphane is to coordinate with the probiotics such as Butyricicoccus. In summary, these findings proved that sulforaphane might be a useful content and serve as a potential therapy in the treatment of UC.
Keywords: Gut dysbiosis; Sulforaphane; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- de Cruz P, Kang S, Wagner J, Buckley M, Sim WH, Prideaux L, Lockett T, Mcsweeney C, Morrison M, Kirkwood CD, Kamm MA. Association between specific mucosa-associated microbiota in Crohn’s disease at the time of resection and subsequent disease recurrence: a pilot study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:268–278. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12694. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

