Emergence of Kawasaki disease related to SARS-CoV-2 infection in an epicentre of the French COVID-19 epidemic: a time-series analysis
- PMID: 32622376
- PMCID: PMC7332278
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30175-9
Emergence of Kawasaki disease related to SARS-CoV-2 infection in an epicentre of the French COVID-19 epidemic: a time-series analysis
Abstract
Background: Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile systemic childhood vasculitis, which is suspected to be triggered by respiratory viral infections. We aimed to examine whether the ongoing COVID-19 epidemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is associated with an increase in the incidence of Kawasaki disease.
Methods: We did a quasi-experimental interrupted time series analysis over the past 15 years in a tertiary paediatric centre in the Paris region, a French epicentre of the COVID-19 outbreak. The main outcome was the number of Kawasaki disease cases over time, estimated by quasi-Poisson regression. In the same centre, we recorded the number of hospital admissions from the emergency department (2005-2020) and the results of nasopharyngeal multiplex PCR to identify respiratory pathogens (2017-2020). These data were compared with daily hospital admissions due to confirmed COVID-19 in the same region, recorded by Public Health France.
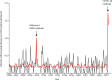
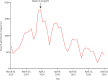
Findings: Between Dec 1, 2005, and May 20, 2020, we included 230 patients with Kawasaki disease. The median number of Kawasaki disease hospitalisations estimated by the quasi-Poisson model was 1·2 per month (IQR 1·1-1·3). In April, 2020, we identified a rapid increase of Kawasaki disease that was related to SARS-CoV-2 (six cases per month; 497% increase [95% CI 72-1082]; p=0·0011), starting 2 weeks after the peak of the COVID-19 epidemic. SARS-CoV-2 was the only virus circulating intensely during this period, and was found in eight (80%) of ten patients with Kawasaki disease since April 15 (SARS-CoV-2-positive PCR or serology). A second peak of hospital admissions due to Kawasaki disease was observed in December, 2009 (six cases per month; 365% increase ([31-719]; p=0.0053), concomitant with the influenza A H1N1 pandemic.
Interpretation: Our study further suggests that viral respiratory infections, including SAR-CoV-2, could be triggers for Kawasaki disease and indicates the potential timing of an increase in incidence of the disease in COVID-19 epidemics. Health-care providers should be prepared to manage an influx of patients with severe Kawasaki disease, particularly in countries where the peak of COVID-19 has recently been reached.
Funding: French National Research Agency.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 era: a distinct clinical phenotype?Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020 Sep;4(9):642-643. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30207-8. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020. PMID: 32622377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

