Lrrk2 modulation of Wnt signaling during zebrafish development
- PMID: 32623786
- PMCID: PMC7643907
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.24687
Lrrk2 modulation of Wnt signaling during zebrafish development
Abstract
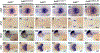
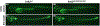
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (lrrk2) are the most common genetic cause of Parkinson's disease. Difficulty in elucidating the pathogenic mechanisms resulting from disease-associated Lrrk2 variants stems from the complexity of Lrrk2 function and activities. Lrrk2 contains multiple protein-protein interacting domains, a GTPase domain, and a kinase domain. Lrrk2 is implicated in many cellular processes including vesicular trafficking, autophagy, cytoskeleton dynamics, and Wnt signaling. Here, we generated a zebrafish lrrk2 allelic series to study the requirements for Lrrk2 during development and to dissect the importance of its various domains. The alleles are predicted to encode proteins that either lack all functional domains (lrrk2sbu304 ), the GTPase, and kinase domains (lrrk2sbu71 ) or the kinase domain (lrrk2sbu96 ). All three lrrk2 mutants are viable, morphologically normal, and display wild-type-like locomotion. Because Lrrk2 modulates Wnt signaling in some contexts, we assessed Wnt signaling in all three mutant lines. Analysis of Wnt signaling by studying the expression of target genes using whole mount RNA in situ hybridization and a transgenic Wnt reporter revealed wild-type domains of Wnt activity in each of the mutants. However, we found that Wnt pathway activation is attenuated in lrrk2sbu304/sbu304 , which lacks both scaffolding and catalytic domains, but not in the other alleles during late embryogenesis. This supports a model in which Lrrk2 scaffolding functions are key to a context-dependent role in promoting canonical Wnt signaling.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Lrrk2; Parkinson's disease; Wnt; zebrafish.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures



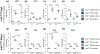
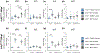
Similar articles
-
Pathogenic LRRK2 variants are gain-of-function mutations that enhance LRRK2-mediated repression of β-catenin signaling.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Jan 19;12(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0153-4. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28103901 Free PMC article.
-
A proteomic analysis of LRRK2 binding partners reveals interactions with multiple signaling components of the WNT/PCP pathway.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Jul 11;12(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0193-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28697798 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of LRRK2 in Zebrafish leads to hyperactivity and weakened antibacterial response.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Mar 18;497(4):1104-1109. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.186. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29499195
-
The role of LRRK2 in cell signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):197-207. doi: 10.1042/BST20180464. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30578345 Review.
-
Understanding the GTPase Activity of LRRK2: Regulation, Function, and Neurotoxicity.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;14:71-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49969-7_4. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28353279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of lrrk2 causes early developmental abnormalities and age-dependent increase of monoamine catabolism in the zebrafish brain.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 13;17(9):e1009794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009794. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34516550 Free PMC article.
-
Fish Models for Exploring Mitochondrial Dysfunction Affecting Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 11;24(8):7079. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087079. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

