Design of stable metabolic networks
- PMID: 32624839
- PMCID: PMC6999264
- DOI: 10.1002/elsc.201700065
Design of stable metabolic networks
Abstract
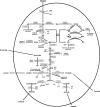
In this work, we propose eigenvalue optimization combined with Lyapunov theory concepts to ensure stability of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway, the pentose-phosphate pathway, the phosphotransferase system and fermentation reactions of Escherichia coli. We address the design of a metabolic network for the maximization of different metabolite production rates. The first case study focuses on serine production, based on a model that consists of 18 differential equations corresponding to dynamic mass balances for extracellular glucose and intracellular metabolites, and thirty kinetic rate expressions. A second case study addresses the design problem to maximize ethanol production, based on a dynamic model that involves mass balances for 25 metabolites and 38 kinetic rate equations. The nonlinear optimization problem including stability constraints has been solved with reduced space Successive Quadratic Programming techniques. Numerical results provide useful insights on the stability properties of the studied kinetic models.
Keywords: Eigenvalue optimization; Metabolic networks; Non‐linear dynamic models; Optimal design; Stability.
© 2017 WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




References
-
- Diaz Ricci, J. C. , Influence of phosphoenolpyruvate on the dynamic behavior of phosphofructokinase of Escherichia coli . J. Theor. Biol. 1996, 178, 145–150.
-
- Hatzimanikatis, V. , Bailey, J. , Studies on glycolysis.1. Multiple steady states in bacterial glycolysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 2579–2588.
-
- Haddad, W. , Chellaboina, V. , Stability and dissipativity theory for nonnegative dynamical systems: A unified analysis framework for biological and physiological systems. Nonlinear Analysis‐Real World Appl. 2005, 6, 33–65.
-
- Ivanov, O. , Schaft, A. , Weissing, F. , Steady states and stability in metabolic networks without regulation. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 401, 78–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
