Application of cationic polymer micelles for the dispersal of bacterial biofilms
- PMID: 32624888
- PMCID: PMC6999407
- DOI: 10.1002/elsc.201800040
Application of cationic polymer micelles for the dispersal of bacterial biofilms
Abstract
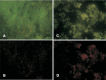
Contamination of surfaces in hospitals and food industry by bacterial biofilms is a serious health risk. Of concern is their resistance to routine antibacterials and disinfectants. This requires the development of novel approaches to biofilm detachment. The study evaluates the effectiveness of cationic polymer micelles (CPMs) against pre-formed biofilms. CPMs based on different polycations were used. The hydrodynamic radius of the particles ranged from 16 to 360 nm. Biofilms of Escherichia coli 420, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, Staphylococcus aureus 29213 and Bacillus subtilis 168 were cultivated for 24 h then the pre-formed biofilms were treated with the CPMs for 2, 4 or 6 h. Biofilm biomass was evaluated by the crystal violet assay, and live/dead fluorescence test was applied for bacterial viability. The ability of CPMs to interact with pre-formed biofilms of the model strains was evaluated. We observed that the most effective CPMs were those based on poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) copolymers which reduced the biofilm biomass three- to four-fold compared with the treatment of the biofilm with water. Significantly reduced vitality of the bacteria in the biofilms was registered by the live/dead stain. The results indicate the applicability of the CPMs for disinfection of biofilm-contaminated surfaces and the treatment of wounds.
Keywords: Bacterial biofilm dispersal; Cationic polymer micelles.
© 2018 WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Schönborn, S. , Krömker, V. , Detection of the biofilm component polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in Staphylococcus aureus infected cow udders. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 196, 126–128. - PubMed
-
- Wood, T. K. Biofilm dispersal: deciding when it is better to travel. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 94, 747–750. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
