Metformin Protects From Rotenone-Induced Nigrostriatal Neuronal Death in Adult Mice by Activating AMPK-FOXO3 Signaling and Mitigation of Angiogenesis
- PMID: 32625061
- PMCID: PMC7314970
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00084
Metformin Protects From Rotenone-Induced Nigrostriatal Neuronal Death in Adult Mice by Activating AMPK-FOXO3 Signaling and Mitigation of Angiogenesis
Abstract
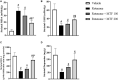
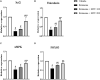
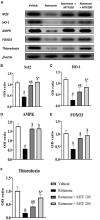
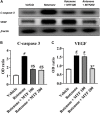
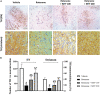
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease that affects substantia nigra dopamine neurons. Many studies have documented the role of oxidative stress and angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of PD. Metformin (MTF) is an antidiabetic medication and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator that has shown antioxidant and antiangiogenic properties in many disorders. The aim of this study is to investigate the neuroprotective effect of MTF in a mouse model of rotenone-prompted PD with a highlight on its influence on the AMPK/forkhead box transcription factor O3 (FOXO3) pathway and striatal angiogenesis. In the running study, PD was induced in mice using repeated doses of rotenone and concomitantly treated with MTF 100 or 200 mg/kg/day for 18 days. Rotarod and pole tests were used to examine the animals' motor functionality. After that, animals were sacrificed, and brains were isolated and processed for immunohistochemical investigations or biochemical analyses. Oxidant stress and angiogenic markers were measured, including reduced glutathione, malondialdehyde, the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), hemoxygenase-1, thioredoxin, AMPK, FOXO3, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Results indicated that MTF improved animals' motor function, improved striatal glutathione, Nrf2, hemoxygenase-1, and thioredoxin. Furthermore, MTF upregulated AMPK-FOXO3 proteins and reduced VEGF and cleaved caspase 3. MTF also increased the number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-stained neurons in the substantia nigra neurons and in striatal neuronal terminals. This study is the first to highlight that the neuroprotective role of MTF is mediated through activation of AMPK-FOXO3 signaling and inhibition of the proangiogenic factor, VEGF. Further studies are warranted to confirm this mechanism in other models of PD and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: AMPK-FOXO3; cleaved caspase 3; metformin; oxidative stress; rotenone-induced parkinsonism; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Copyright © 2020 El-Ghaiesh, Bahr, Ibrahiem, Ghorab, Alomar, Farag and Zaitone.
Figures


References
-
- Ahuja M., Ammal Kaidery N., Yang L., Calingasan N., Smirnova N., Gaisin A., et al. (2016). Distinct Nrf2 signaling mechanisms of fumaric acid esters and their role in neuroprotection against 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced experimental Parkinson’s-like disease. J. Neurosci. 36 6332–6351. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0426-16.2016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani S., Ezzat W., Elshaer R. E., Abd El-Lateef A. S., Mohammad H. M. F., Elkazaz A. Y., et al. (2018). Standarized Tribulus terrestris extract protects against rotenone-induced oxidative damage and nigral dopamine neuronal loss in mice. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 69 979–994. 10.26402/jpp.2018.6.14 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonella N., Fabio C. (2005). Role of inflammatory mediators in angiogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 4 3–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

