Re-evaluation of sorbitan monostearate (E 491), sorbitan tristearate (E 492), sorbitan monolaurate (E 493), sorbitan monooleate (E 494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E 495) when used as food additives
- PMID: 32625491
- PMCID: PMC7010202
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4788
Re-evaluation of sorbitan monostearate (E 491), sorbitan tristearate (E 492), sorbitan monolaurate (E 493), sorbitan monooleate (E 494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E 495) when used as food additives
Abstract
The Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS) provides a scientific opinion re-evaluating the safety of sorbitan monostearate (E 491), sorbitan tristearate (E 492), sorbitan monolaurate (E 493), sorbitan monooleate (E 494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E 495) when used as food additives. The Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) allocated an acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 25 mg/kg body weight (bw) per day for E 491, E 492 and E 495 singly or in combination; and a separate group ADI for E 493 and E 494 singly or in combination of 5 mg/kg bw per day calculated as sorbitan monolaurate in 1974. The Panel noted that after oral administration sorbitan monostearate can be either hydrolysed to its fatty acid moiety and the corresponding anhydrides of sorbitol and excreted via urine or exhaled as CO 2 or excreted intact in the faeces. The Panel considered that sorbitan esters did not raise concern for genotoxicity. Based on the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) of 2,600 mg sorbitan monostearate/kg bw per day, taking into account the ratio between the molecular weight of sorbitan monostearate (430.62 g/mol) and sorbitan (164.16 g/mol), and applying an uncertainty factor of 100, the Panel derived a group ADI of 10 mg/kg bw per day expressed as sorbitan for sorbitan esters (E 491-495) singly or in combination. This group ADI of 10 mg sorbitan/kg bw per day is equivalent to 26 mg sorbitan monostearate/kg bw per day. The Panel concluded that the exposure at the mean and the 95th percentile level, using non-brand-loyal scenario, did not exceed the ADI in any of the population groups. The Panel on the request for an amendment of specifications regarding the removal of 'congealing range' concluded that it could be eventually replaced by another identification parameter such as melting point.
Keywords: food additive; sorbitan esters; sorbitan monolaurate; sorbitan monooleate and sorbitan monopalmitate; sorbitan monostearate; sorbitan tristearate.
© 2017 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
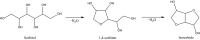

(a) The Panel noted that in Figure 1 only 1 (sorbitan form) out of three forms (sorbitol, sorbitan and isosorbide esters) is presented.
References
-
- Anneken DJ, Both S, Christoph R, Fieg G, Steinberner U and Westfechtel A, 2012. Fatty acids. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 14, 73–116.
-
- Benigni R, Bossa C and Worth A, 2010. Structural analysis and predictive value of the rodent in vivo micronucleus assay results. Mutagenesis, 25, 335–341. - PubMed
-
- Benigni R, Bossa C, Tcheremenskaia O, Battistelli CL and Crettaz P, 2012. The new ISSMIC database on in vivo micronucleus and its role in assessing genotoxicity testing strategies. Mutagenesis, 27, 87–92. - PubMed
-
- Burch R, Topping J and Haines J, 2007. Final report for food standards agency: Review of literature relating to the extraction of additives from complex food matrices. Project number A01058.
-
- Cani PD and Everard A, 2015. Keeping gut lining at bay: impact of emulsifiers. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 26, 273–274. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
