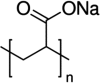
Safety assessment of the active substance polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked, for use in active food contact materials
- PMID: 32625741
- PMCID: PMC7009422
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5448
Safety assessment of the active substance polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked, for use in active food contact materials
Abstract
The EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP) assessed the safety of polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked, FCM substance No 1015, which is intended to be used as a liquid absorber in the packaging of fresh or frozen foods such as meat, poultry and seafood as well as fresh fruits and vegetables. Specific migration tests were not performed due to the high absorption of liquids by the substance. The Panel noted that if polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked is used not in direct contact with food and placed in a pad under conditions where its absorption capacity is not exceeded, then no migration is to be expected and therefore no exposure from the consumption of the packed food is expected. The Panel also considered that the non-cross-linked polymer and the cross-linkers do not raise a concern for genotoxicity. The CEP Panel concluded that the use of this polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, cross-linked, does not raise a safety concern when used in absorbent pads in the packaging of fresh or frozen foods. The absorbent pads must be used only under conditions in which the absorption capacity of the active substance is not exceeded and direct contact with food is excluded.
Keywords: FCM substance No 1015; active and intelligent materials; food contact materials; liquid absorber; polyacrylic acid sodium salt cross‐linked.
© 2018 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
References
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2009. Guidance of the Scientific Committee on transparency in the scientific aspects of risk assessments carried out by EFSA. Part 2: general principles. EFSA Journal 2009;7 (5):1051, 22 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1051 - DOI
-
- ■■■■■
-
- ■■■■■
-
- EFSA CEF Panel (EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes, Flavourings and Processing Aids), 2009. Guidelines on submission of a dossier for safety evaluation by the EFSA of active or intelligent substances present in active and intelligent materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. EFSA Journal 2009;7(8):1208, 11 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1208 - DOI
-
- EFSA CEF Panel (EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes, Flavourings and Processing Aids), 2014. Scientific Opinion on safety assessment of the active substance, polyacrylic acid, sodium salt, crosslinked, for use in active food contact materials. EFSA Journal 2014;12(5):3648, 9 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3648 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources