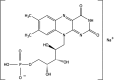
Safety and efficacy of vitamin B2 (riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt) for all animal species when used in water for drinking
- PMID: 32625794
- PMCID: PMC7009649
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5531
Safety and efficacy of vitamin B2 (riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt) for all animal species when used in water for drinking
Abstract
Following a request from the European Commission, the Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) was asked to deliver a scientific opinion on vitamin B2 in the form of riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt as an additive for all animal species for use in water for drinking. The additive under assessment is obtained from ■■■■■ a source of riboflavin produced by Ashbya gossypii. No information was provided on the identity and characterisation of the production strain, and on whether or not it is a genetically modified microorganism. Therefore, in the absence of adequate information, it is not possible to perform an assessment of the safety of the production strain. Riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt 'per se' is considered safe for the target animals, consumers and the environment. In the absence of data regarding the identity and characterisation of the production strain, the FEEDAP Panel cannot conclude on the safety for the target species, consumers, users and the environment of the riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt under assessment. Similarly, in the absence of data, no conclusion can be reached on the safety of the product for the users. Riboflavin 5'-phosphate ester monosodium salt is regarded as effective in covering the animal's requirement when administered via water for drinking.
Keywords: nutritional additive; riboflavin; riboflavin 5′‐phosphate ester monosodium salt; vitamin B2; vitamins and provitamins.
© 2018 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
References
-
- AWT (Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Wirkstoffe in der Tierernährung e.V.), 2002. Vitamins in animal nutrition, Agrimedia GmbH, ISBN 3‐86037‐167‐3.
-
- Cardoso DR, Libardi SH and Skibsted LH, 2012. Riboflavin as a photosensitizer. Effects on human health and food quality. Food & Function, 3, 487–502. - PubMed
-
- Christensen S, 1969. Studies on Riboflavin metabolism in the rat. I. Urinary and faecal excretion after oral administration of Riboflavin‐5′‐phosphate. Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica, 27, 34–40. - PubMed
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008a. Guidance of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) for the preparation of dossiers for the re‐evaluation of certain additives already authorised under Directive 70/524/EEC. EFSA Journal 2008;6(9):779, 9 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.779 - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008b. Technical Guidance of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) for assessing the safety of feed additives for the environment. EFSA Journal 2008;6(10):842, 28 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.842 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources