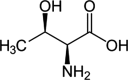
Safety and efficacy of l-threonine produced by fermentation with Corynebacterium glutamicum ■■■■■ for all animal species
- PMID: 32626227
- PMCID: PMC7009064
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5602
Safety and efficacy of l-threonine produced by fermentation with Corynebacterium glutamicum ■■■■■ for all animal species
Abstract
Following a request from the European Commission, the Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) was asked to deliver a scientific opinion on l-threonine produced by fermentation with Corynebacterium glutamicum ■■■■■ when used as a nutritional additive in feed and water for drinking for all animal species and categories. The product under assessment is l-threonine produced by fermentation with a ■■■■■ strain of C. glutamicum (■■■■■). l-Threonine produced by C. glutamicum ■■■■■ is considered safe for the target species when supplemented in appropriate amounts to the diet. The FEEDAP Panel has concerns on the safety of the simultaneous oral administration of l-threonine via water for drinking and feed. l-Threonine produced using C. glutamicum ■■■■■ is safe for the consumer. The additive is not a skin or eye irritant and is not a skin sensitiser. Although the workers can be exposed by inhalation, the results of an acute inhalation study showed that risk of adverse effects by inhalation is low. l-Threonine produced using C. glutamicum ■■■■■ is safe for the environment. The product under assessment is considered an efficacious source of the amino acid l-threonine for all animal species. For l-threonine to be as efficacious in ruminants as in non-ruminant species, it requires protection against degradation in the rumen.
Keywords: Corynebacterium glutamicum; amino acid; efficacy; l‐threonine; nutritional additive; safety.
© 2019 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
References
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008. Technical Guidance of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) for assessing the safety of feed additives for the environment. EFSA Journal 2008;6(10):842, 28 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.842 - DOI
-
- EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards), Koutsoumanis K, Allende A, Alvarez‐Ordonez A, Bolton D, Bover‐Cid S, Chemaly M, Davies R, Hilbert F, Lindqvist R, Nauta M, Peixe L, Ru G, Simmons M, Skandamis P, Suffredini E, Cocconcelli PS, Fernandez Escamez PS, Maradona MP, Querol A, Suarez JE, Sundh I, Vlak J, Barizzone F, Correia S and Herman L, 2019. Statement on the update of the list of QPS‐recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 9: suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until September 2019. EFSA Journal 2019;17(1):5555, 46 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5555 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed), 2010. Scientific Opinion on the use of feed additives authorised/applied for use in feed when supplied via water. EFSA Journal 2010;8(12):1956, 9 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1956 - DOI
-
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed), 2012a. Guidance for the preparation of dossiers for nutritional additives. EFSA Journal 2012;10(1):2535, 14 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2535 - DOI
-
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed), 2012b. Guidance on studies concerning the safety of use of the additive for users/workers. EFSA Journal 2012;10(1):2539, 5 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2539 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources