Safety and efficacy of l-valine produced using Corynebacterium glutamicum CGMCC 11675 for all animal species
- PMID: 32626243
- PMCID: PMC7009085
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5611
Safety and efficacy of l-valine produced using Corynebacterium glutamicum CGMCC 11675 for all animal species
Abstract
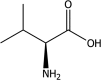
The product subject of this assessment is l-valine produced by fermentation with a strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum (CGMCC 11675). It is intended to be used in feed and water for drinking for all animal species and categories. Owing to the uncertainties regarding the possible genetic modification of the original production strain, the FEEDAP Panel cannot conclude on the safety of the additive l-valine produced with C. glutamicum CGMCC 11675 for the target species, the consumers, the users and the environment. The FEEDAP Panel has concerns on the safety for the target animals of the simultaneous oral administration of valine-containing additives via feed and water for drinking. In the absence of data, the FEEDAP Panel cannot conclude on the potential of l-valine produced with C. glutamicum CGMCC 11675 to be toxic by inhalation, irritant to skin or eyes, or on its potential to be a dermal sensitiser. The product is considered an efficacious source of the amino acid l-valine for all animal species. The supplemental l-valine requires protection against rumen degradations in order to be as efficacious in ruminant as in non-ruminant species.
Keywords: amino acids and their salts and analogues; efficacy; genetically modified microorganisms; l‐valine; nutritional additives; safety.
© 2019 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
References
-
- Broderick GA and Balthrop JE, 1979. Chemical inhibition of amino acid deamination by ruminal microbes in vitro. Journal of Animal Science, 49, 1101–1111.
-
- Chalupa W, 1976. Degradation of amino acids by the mixed rumen microbial population. Journal of Animal Science, 43, 828–834. - PubMed
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2007. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on a request from EFSA on the introduction of a Qualified Presumption of Safety (QPS) approach for assessment of selected microorganisms referred to EFSA. EFSA Journal 2007;5(12):587, 16 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2007.587 - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008a. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) and of the Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) on the efficacy and the safety of L‐valine from a modified E. coli K12 for all animal species. EFSA Journal 2008;6(5):695, 21 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.695 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources