Safety and efficacy of sorbitan monolaurate as a feed additive for all animal species
- PMID: 32626271
- PMCID: PMC7009278
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5651
Safety and efficacy of sorbitan monolaurate as a feed additive for all animal species
Abstract
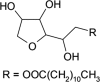
The additive sorbitan monolaurate consists of sorbitol (and its anhydrides) esterified with fatty acids derived from coconut oil. It is intended to be used as a technological additive, functional group: emulsifier, in feedingstuffs for all animal species, at a maximum concentration of 85 mg/kg complete feed. The EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) concluded that sorbitan monolaurate is safe for all animal species at the proposed maximum content of 85 mg/kg complete feed and that the use of sorbitan monolaurate in animal nutrition is not expected to pose a risk for the consumer under the proposed conditions of use. Users are unlikely to be exposed to sorbitan monolaurate via inhalation. Sorbitan monolaurate is irritant to skin and eyes and it is not considered a skin sensitiser. Owing the lack of data, the FEEDAP Panel cannot conclude on the safety of the additive for the environment. Sorbitan monolaurate is authorised for use as a food additive with the function of emulsifier. The technological effect underlying its use as a food additive could reasonably be expected to be seen when used in feed.
Keywords: efficacy; emulsifiers; safety; sorbitan monolaurate; technological additives.
© 2019 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
References
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008a. Technical Guidance of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) for assessing the safety of feed additives for the environment. EFSA Journal 2008,6(10):842, 28 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.842 - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), 2008b, revised in 2009. Guidance of the Scientific Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) for the preparation of dossiers for the re‐evaluation of certain additives already authorised under Directive 70/524/EEC. EFSA Journal 2008,6(9):779, 9 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.779 - DOI
-
- EFSA ANS Panel (EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food), 2017. Scienti fic Opinion on the re‐evaluation of sorbitan monostearate (E 491), sorbitan tristearate (E 492), sorbitan monolaurate (E 493), sorbitan monooleate (E 494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E 495) when used as food additives. EFSA Journal 2017;15(5):4788, 56 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4788 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed), 2011. Technical guidance: Tolerance and efficacy studies in target animals. EFSA Journal 2011;9(5):2175, 15 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2175 - DOI
-
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed), 2012a. Guidance for the preparation of dossiers for technological additives. EFSA Journal 2012;10(1):2528, 23 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2528 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources