Guidance on the assessment of the safety of feed additives for the environment
- PMID: 32626279
- PMCID: PMC7009194
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5648
Guidance on the assessment of the safety of feed additives for the environment
Abstract
This guidance document is intended to assist the applicant in the preparation and the presentation of an application, as foreseen in Article 7.6 of Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003, for the authorisation of additives used in animal nutrition. It specifically covers the assessment of the safety for the environment. [Table: see text].
Keywords: environment; feed additives; guidance; risk assessment.
© 2019 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
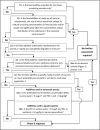
*PEC in ground water is set equal to PEC in pore water (see Section 2.6.2).
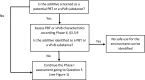
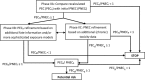

References
-
- Arnot J, Gouin T and Mackay D, 2005. Practical Methods for Estimating Environmental Biodegradation Rates, Report to Environment Canada. CEMN Report No 200503. Canadian Environmental Modelling Network, Trent University, Peterborough, ON, Canada.
-
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), 2007. E1611. Standard Guide for Conducting Sediment Toxicity Tests with Polychaetous Annelids. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
-
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), 2010a. E1706‐05. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Toxicity of Sediment‐Associated Contaminants with Freshwater Invertebrates. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
-
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), 2010b. E1367‐03. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Toxicity of Sediment‐Associated Contaminants with Estuarine and Marine Invertebrates. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
-
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), 2014. E1367‐03. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Toxicity of Sediment‐Associated Contaminants with Estuarine and Marine Invertebrates, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2014, http://www.astm.org 10.1520/e1367-03r14 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
