Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Overcome Resistance to Targeted and Immuno Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma
- PMID: 32626712
- PMCID: PMC7311641
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00486
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Overcome Resistance to Targeted and Immuno Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma
Abstract
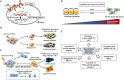
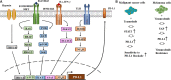
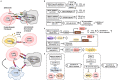
Therapies that target oncogenes and immune checkpoint molecules constitute a major group of treatments for metastatic melanoma. A mutation in BRAF (BRAF V600E) affects various signaling pathways, including mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in melanoma. Target-specific agents, such as MAPK inhibitors improve progression-free survival. However, BRAFV600E mutant melanomas treated with BRAF kinase inhibitors develop resistance. Immune checkpoint molecules, such as programmed death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand-1(PD-L1), induce immune evasion of cancer cells. MAPK inhibitor resistance results from the increased expression of PD-L1. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-1, are main players in immune therapies designed to target metastatic melanoma. However, melanoma patients show low response rate and resistance to these inhibitors develops within 6-8 months of treatment. Epigenetic reprogramming, such as DNA methylaion and histone modification, regulates the expression of genes involved in cellular proliferation, immune checkpoints and the response to anti-cancer drugs. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) remove acetyl groups from histone and non-histone proteins and act as transcriptional repressors. HDACs are often dysregulated in melanomas, and regulate MAPK signaling, cancer progression, and responses to various anti-cancer drugs. HDACs have been shown to regulate the expression of PD-1/PD-L1 and genes involved in immune evasion. These reports make HDACs ideal targets for the development of anti-melanoma therapeutics. We review the mechanisms of resistance to anti-melanoma therapies, including MAPK inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors. We address the effects of HDAC inhibitors on the response to MAPK inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. In addition, we discuss current progress in anti-melanoma therapies involving a combination of HDAC inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and MAPK inhibitors.
Keywords: HDACs; MAPK; anti-cancer drug resistance; immune checkpoint; melanoma.
Copyright © 2020 Yeon, Kim, Jung and Jeoung.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Future perspectives in melanoma research: meeting report from the "Melanoma Bridge": Napoli, December 3rd-6th 2014.J Transl Med. 2015 Nov 30;13:374. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0736-1. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26619946 Free PMC article.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the MAPK and PI3K pathways in combination with PD1 blockade in melanoma.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Oct 14;5(12):e1238557. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1238557. eCollection 2016. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 28123875 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3K inhibition.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 1;19(3):598-609. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2731. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23095323
-
Resistance to combination BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic melanoma: Where to next?Eur J Cancer. 2016 Jul;62:76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 24. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27232329 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors: A Promising Weapon to Tackle Therapy Resistance in Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 27;23(7):3660. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073660. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pilot study on the efficacy of a telomerase activator in regulating the proliferation of A375 skin cancer cell line.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 20;52(1):69. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10161-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39704853
-
Photocaged Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Prodrugs in Targeted Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 25;16(3):356. doi: 10.3390/ph16030356. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986455 Free PMC article.
-
SNAI2 cooperates with MEK1/2 and HDACs to suppress BIM- and BMF-dependent apoptosis in TERT promoter mutant cancers.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0322961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322961. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40560846 Free PMC article.
-
Thinking Small: Small Molecules as Potential Synergistic Adjuncts to Checkpoint Inhibition in Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3228. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063228. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ascierto P. A., Dummer R., Gogas H. J., Flaherty K. T., Arance A., Mandala M., et al. (2020a). Update on tolerability and overall survival in COLUMBUS: landmark analysis of a randomised phase 3 trial of encorafenib plus binimetinib vs vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF V600-mutant melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 126 33–44. 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.11.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

