Placental exosomes isolated from urine of patients with gestational diabetes exhibit a differential profile expression of microRNAs across gestation
- PMID: 32626972
- PMCID: PMC7307810
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4626
Placental exosomes isolated from urine of patients with gestational diabetes exhibit a differential profile expression of microRNAs across gestation
Abstract
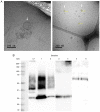
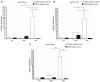
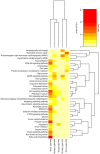
Placenta‑derived exosomes play an important role in cellular communication both in the mother and the fetus. Their concentration and composition are altered in several pregnancy disorders, such as gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). The isolation and characterization of placental exosomes from serum, plasma and tissues from patients with GDM have been previously described; however, to the best of our knowledge, to date, there is no study available on placental exosomes isolated from urine of patients with GDM. In the present study, placental exosomes were purified from urine the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester of gestation. Placental exosomes were characterized by transmission electron microscopy in cryogenic mode and by western blot analysis, confirming the presence of exosomal vesicles. The expression profile of five microRNAs (miR‑516‑5p, miR‑517‑3p, miR‑518‑5p, miR‑222‑3p and miR‑16‑5p) was determined by RT‑qPCR. In healthy pregnant women, the expression of the miRNAs increased across gestation, apart from miR‑516‑5p, which was not expressed at the 2nd trimester. All the miRNAs examined were downregulated in patients with GDM at the 3rd trimester of gestation. The downregulated miRNAs affected several metabolic pathways closely associated with the pathophysiology of GDM. This provides further evidence of the regulatory role of miRNAs in the GDM. This also suggests that the of urinary exosomes may be an excellent source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early-Pregnancy Serum Maternal and Placenta-Derived Exosomes miRNAs Vary Based on Pancreatic β-Cell Function in GDM.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 May 17;109(6):1526-1539. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad751. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38127956
-
Human placental exosomes in gestational diabetes mellitus carry a specific set of miRNAs associated with skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Nov 29;132(22):2451-2467. doi: 10.1042/CS20180487. Print 2018 Nov 30. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30254065
-
Review: Bio-compartmentalization of microRNAs in exosomes during gestational diabetes mellitus.Placenta. 2017 Jun;54:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Placenta. 2017. PMID: 27939101 Review.
-
Adipose Tissue Exosomal Proteomic Profile Reveals a Role on Placenta Glucose Metabolism in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 May 1;104(5):1735-1752. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01599. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30517676
-
MiRNAs in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Nov 24;2021:4632745. doi: 10.1155/2021/4632745. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34869778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Emerging Roles as Cellular Messengers in Endocrinology: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement.Endocr Rev. 2022 May 12;43(3):441-468. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnac009. Endocr Rev. 2022. PMID: 35552682 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes: The role in mammalian reproductive regulation and pregnancy-related diseases.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 10;14:1056905. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1056905. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36969587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placenta-derived exosomal miR-135a-5p promotes gestational diabetes mellitus pathogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT signalling pathway via SIRT1.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Dec;27(23):3729-3743. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17941. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37667545 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Circulating C19MC MicroRNA as an Early Marker of Hypertension and Preeclampsia in Pregnant Patients: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 29;11(23):7051. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237051. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placenta-Derived Exosomes as a Modulator in Maternal Immune Tolerance During Pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 11;12:671093. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.671093. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34046039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basina M. Gestational diabetogenesis. J Women's Health Care. 2012;01:e106. doi: 10.4172/2167-0420.1000e106. - DOI

