Kidney transplant patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The Brescia Renal COVID task force experience
- PMID: 32627319
- PMCID: PMC7361317
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16176
Kidney transplant patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The Brescia Renal COVID task force experience
Abstract
The outcome of kidney transplant patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is still unclear. Here we describe the clinical characteristics, disease outcome, and risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death of a cohort of 53 kidney transplant patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Eight of 53 have been handled as outpatients because of mild disease, on average with immunosuppression reduction and the addition of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin; no patients required admission, developed ARDS, or died. Because of severe symptoms, 45/53 required admission: this cohort has been managed with immunosuppression withdrawal, methylprednisolone 16 mg/d, hydroxychloroquine, and antiviral drugs. Dexamethasone and tocilizumab were considered in case of ARDS. About 33% of the patients developed acute kidney injury, 60% ARDS, and 33% died. In this group, thrombocytopenia was associated to ARDS whereas lymphopenia at the baseline, higher D-dimer, and lack of C-reactive protein reduction were associated with risk of death. In the overall population, dyspnea was associated with the risk of ARDS and age older than 60 years and dyspnea were associated with the risk of death with only a trend toward an increased risk of death for patients on tacrolimus. In conclusion, SARS-CoV-2 infection may have a variable outcome in renal transplant patients, with higher risk of ARDS and death in the ones requiring admission.
Keywords: clinical research/practice; infection and infectious agents - viral; infectious disease; kidney disease: infectious.
© 2020 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures

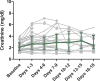
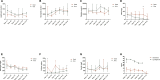
References
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force. Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526–2533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

