Phase 3 trial of human islet-after-kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 32627352
- PMCID: PMC9074710
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16174
Phase 3 trial of human islet-after-kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
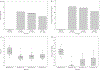
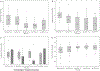
Allogeneic islet transplant offers a minimally invasive option for β cell replacement in the treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D). The CIT consortium trial of purified human pancreatic islets (PHPI) in patients with T1D after kidney transplant (CIT06), a National Institutes of Health-sponsored phase 3, prospective, open-label, single-arm pivotal trial of PHPI, was conducted in 24 patients with impaired awareness of hypoglycemia while receiving intensive insulin therapy. PHPI were manufactured using standardized processes. PHPI transplantation was effective with 62.5% of patients achieving the primary endpoint of freedom from severe hypoglycemic events and HbA1c ≤ 6.5% or reduced by ≥ 1 percentage point at 1 year posttransplant. Median HbA1c declined from 8.1% before to 6.0% at 1 year and 6.3% at 2 and 3 years following transplant (P < .001 for all vs baseline), with related improvements in hypoglycemia awareness and glucose variability. The improved metabolic control was associated with better health-related and diabetes-related quality of life. The procedure was safe and kidney allograft function remained stable after 3 years. These results add to evidence establishing allogeneic islet transplant as a safe and effective treatment for patients with T1D and unstable glucose control despite intensive insulin treatment, supporting the indication for PHPI in the post-renal transplant setting.
Keywords: basic (laboratory) research/science; clinical research/practice; diabetes; diabetes: type 1; islet transplantation.
© 2020 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
The authors of this manuscript have conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
No other potential dualities of interest relative to this manuscript were reported.
Figures



Comment in
-
Islet or pancreas after kidney transplantation: Is the whole still greater than some of its parts?Am J Transplant. 2021 Apr;21(4):1363-1364. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16232. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 32743962 No abstract available.
References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: considerations for allogeneic pancreatic islet cell products (article online). 2009; Available from https://www.fda.gov/media/77497/download. Accessed 20 October 2015
-
- Tiwari JL, Schneider B, Barton F, Anderson SA. Islet cell transplantation in type 1 diabetes: an analysis of efficacy outcomes and considerations for trial designs. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(7):1898–1907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000003/University of Pennsylvania
- U01 AI065192/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000114/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025741/Northwestern University
- U01 DK070460/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK070431/University of Illinois at Chicago
- U01DK070460/University of Miami
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI065193/University of Minnesota
- UL1TR000050/University of Illinois at Chicago
- M01-RR00040/University of Pennsylvania
- U01DK070430/University of Pennsylvania
- U01 AI089316/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000114/University of Minnesota
- U01 AI089317/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK070431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000454/Emory University
- M01-RR000400/University of Minnesota
- UL1TR000150/Northwestern University
- M01 RR000040/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI089316/Northwestern University
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI065192/Uppsala Universitet
- U01 AI065191/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000050/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000460/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI065191/University of Alberta
- U01AI089317/Emory University
- U01 AI065193/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000004/University of California, San Francisco
- UL1TR000460/University of Miami
- U01DK085531/University of California, San Francisco
- U01 DK070430/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

