Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor use and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: A dose-response meta analysis
- PMID: 32627649
- PMCID: PMC7338647
- DOI: 10.1177/1470320319895646
Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor use and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: A dose-response meta analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study was undertaken to determine whether use of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors would increase colorectal cancer morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Databases were electronically searched to collect data of RAS use and colorectal cancer morbidity and mortality from inception to October 2018. Stata 12.0 software was used to perform a meta-analysis.
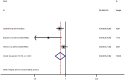
Results: A total of 16 publications involving 2,847,597 participants were included. RAS inhibitor use was related to colorectal cancer risk (relative risk (RR): 0.86; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.78-0.93) and mortality (RR: 0.80; 95% CI: 0.66-0.98) decrement. Subgroup analysis showed angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI)/angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) (RR: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.69-0.96) or ARB (RR: 0.86; 95% CI: 0.73-0.98) or ACEI (RR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.70-0.92) were related to colorectal cancer risk decrement. Furthermore, RAS inhibitor use was related to colorectal cancer risk decrement in Caucasians (RR: 0.88; 95% CI: 0.80-0.96) and Asians (RR: 0.72; 95% CI: 0.61-0.85). Additionally, dose-response showed that per one year duration of RAS inhibitor use incremental increase was related to 6% colorectal cancer risk decrement (RR: 0.94; 95% CI: 0.90-0.97).
Conclusion: According to the evidence, RAS inhibitor use was associated with colorectal cancer risk and mortality decrement.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; dose–response relationship; meta analysis; renin–angiotensin system inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 271–289. - PubMed
-
- Leporrier J, Maurel J, Chiche L, et al. A population-based study of the incidence, management and prognosis of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 2006; 93: 465–474. - PubMed
-
- Gullapalli N, Bloch MJ, Basile J. Renin–angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in high-risk hypertensive patients: Current approaches and future trends. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 2010; 4: 359–373. - PubMed
-
- Bangalore S, Kumar S, Kjeldsen SE, et al. Antihypertensive drugs and risk of cancer: Network meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses of 324,168 participants from randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 65– 82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

