Tartryl-CoA inhibits succinyl-CoA synthetase
- PMID: 32627745
- PMCID: PMC7336359
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X20008201
Tartryl-CoA inhibits succinyl-CoA synthetase
Abstract
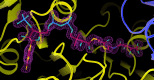
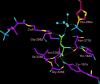
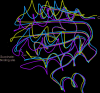
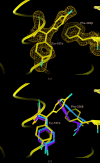
Succinyl-CoA synthetase (SCS) catalyzes the only substrate-level phosphorylation step in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Human GTP-specific SCS (GTPSCS), an αβ-heterodimer, was produced in Escherichia coli. The purified protein crystallized from a solution containing tartrate, CoA and magnesium chloride, and a crystal diffracted to 1.52 Å resolution. Tartryl-CoA was discovered to be bound to GTPSCS. The CoA portion lies in the amino-terminal domain of the α-subunit and the tartryl end extends towards the catalytic histidine residue. The terminal carboxylate binds to the phosphate-binding site of GTPSCS.
Keywords: catalysis; succinyl-CoA synthetase; thioesters; tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Figures



References
-
- Adler, J., Wang, S.-F. & Lardy, H. A. (1957). J. Biol. Chem. 229, 865–879. - PubMed
-
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Kessler, M., Luo, J., Motherwell, W. D. S., Purkis, L. H., Smith, B. R., Taylor, R., Cooper, R. I., Harris, S. E. & Orpen, A. G. (2004). J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44, 2133–2144. - PubMed
-
- Cha, S. & Parks, R. E. Jr (1964). J. Biol. Chem. 239, 1968–1977. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

