Stable and dynamic representations of value in the prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 32628108
- PMCID: PMC7390599
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.54313
Stable and dynamic representations of value in the prefrontal cortex
Abstract
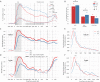
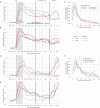
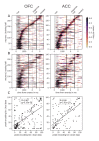
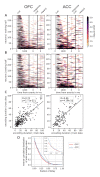
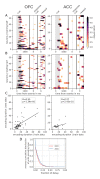
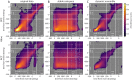
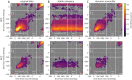
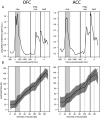
Optimal decision-making requires that stimulus-value associations are kept up to date by constantly comparing the expected value of a stimulus with its experienced outcome. To do this, value information must be held in mind when a stimulus and outcome are separated in time. However, little is known about the neural mechanisms of working memory (WM) for value. Contradicting theories have suggested WM requires either persistent or transient neuronal activity, with stable or dynamic representations, respectively. To test these hypotheses, we recorded neuronal activity in the orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate cortex of two monkeys performing a valuation task. We found that features of all hypotheses were simultaneously present in prefrontal activity, and no single hypothesis was exclusively supported. Instead, mixed dynamics supported robust, time invariant value representations while also encoding the information in a temporally specific manner. We suggest that this hybrid coding is a critical mechanism supporting flexible cognitive abilities.
Keywords: decision-making; neural coding; neuroscience; orbitofrontal cortex; prefrontal cortex; rhesus macaque; value; working memory.
© 2020, Enel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PE, JW, ER No competing interests declared
Figures









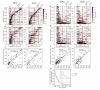

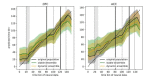
References
-
- Amit DJ. The hebbian paradigm reintegrated: local reverberations as internal representations. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 1995;18:617–626. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X00040164. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

