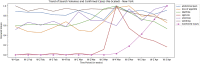
Increased Internet Search Interest for GI Symptoms May Predict COVID-19 Cases in US Hotspots
- PMID: 32629121
- PMCID: PMC7834024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.06.058
Increased Internet Search Interest for GI Symptoms May Predict COVID-19 Cases in US Hotspots
Abstract
Google Trends is an online tool that allows measurement of search term popularity on Google, spatially and temporally. While not an epidemiological tool for determining incidence, it can estimate the popularity of a certain disease by search volume over time.1,2 It has previously correlated well with infectious disease incidence and has demonstrated utility in disease forecasting, especially with influenza data.3 We utilized Google Trends to investigate whether search interest in common gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms would correlate with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) incidence data.
Copyright © 2020 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
COVID-19 Epidemiology and Google Searches.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb;19(2):406-407. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.10.020. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33068785 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Flanagan R., Kuo B., Staller K. Utilizing Google Trends to assess worlwide interest in irritable bowel syndrome and commonly associated treatments. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 May 2 [E-pub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg J., Mohebbi M.H., Patel R.S. Detecting influenza epidemics using search engine query data. Nature. 2008;457:1012–1014. - PubMed
-
- US COVID-19 Daily Cases with Basemap Harvard Dataverse. Version 24.0. https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN... Available at: - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources