Red blood cell exchange to avoid intubating a COVID-19 positive patient with sickle cell disease?
- PMID: 32629539
- PMCID: PMC7361739
- DOI: 10.1002/jca.21809
Red blood cell exchange to avoid intubating a COVID-19 positive patient with sickle cell disease?
Abstract
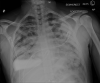
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to claim lives across the globe, insufficient data exists regarding the optimal treatment. It is well known that patients 55 years of age or older and patients with certain chronic diseases are at higher risk of severe illness, including acute respiratory distress syndrome and death. A potentially fatal pulmonary complication of sickle cell disease, acute chest syndrome, can be precipitated by acute infections, including respiratory viruses. We report the case of a patient with sickle cell disease (HbSC) who developed COVID-19 pneumonia and acute chest syndrome who was treated with emergent red blood cell exchange in order to avoid endotracheal intubation.
Keywords: HbSC; SARS-CoV-2; acute chest syndrome.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest relevant to the article.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Situation Report – 92. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/2.... Accessed April 21, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous