Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared from Quaternized Polyepichlorohydrin Cross-Linked with 1-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole Grafted Poly(arylene ether ketone) for Enhancement of Toughness and Conductivity
- PMID: 32629946
- PMCID: PMC7408090
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes10070138
Anion Exchange Membranes Prepared from Quaternized Polyepichlorohydrin Cross-Linked with 1-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole Grafted Poly(arylene ether ketone) for Enhancement of Toughness and Conductivity
Abstract
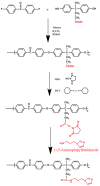
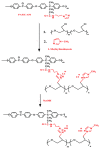
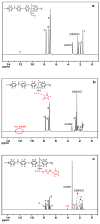
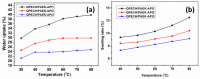
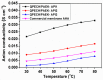
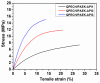
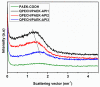
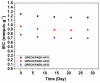
A novel anion exchange membrane was synthesized via crosslinking of the quaternized polyepichlorohydrin (QPECH) by 1-(3-aminopropyl) imidazole grafted poly(arylene ether ketone) (PAEK-API). While the QPECH provided an excellent ion conductive property, the rigid rod-structured PAEK-API played a reinforcing role, along with providing the high conductivity associated with the pendant API group. The chemical structure of QPECH/PAEK-API membranes was identified by 1H nuclear magnetic resonace spectroscopy. A variety of membrane properties, such as anion conductivity, water uptake, length swelling percentage, and thermal, mechanical and chemical stability, were investigated. The QPECH/PAEK-API1 membrane showed quite high hydroxide ion conductivity, from 0.022 S cm-1 (30 °C) to 0.033 S cm-1 (80 °C), and excellent mechanical strength, associated with the low water uptake of less than 40%, even at 80 °C. Such high conductivity at relatively low water uptake is attributed to the concentrated cationic groups, in a cross-linked structure, facilitating feasible ion transport. Further, the QPECH/PAEK-API membranes showed thermal stability up to 250 °C, and chemical stability for 30 days in a 4 NaOH solution, without significant loss of ion exchange capacity.
Keywords: Anion exchange membrane; PAEK; crosslinking; imidazole; ion conductivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hunger H. Ion-exchange liquid-fuel cells; Proceedings of the Annual Power Sources Conference, 1960 U.S. Army Signal REsearch and Development Laboratory, Power Sources Division; Atlantic City, NJ, USA. 17–19 May 1960; pp. 55–59.
-
- Merle G., Wessling M., Nijmeijer K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011;377:1–35. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.04.043. - DOI
-
- Vo D.C.T., Nguyen M.D.T., Kim D. Dual sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) membrane grafted with 15-crown-5-ether for enhanced proton conductivity and anti-oxidation stability. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2019;4:901–911. doi: 10.1039/C9ME00009G. - DOI
-
- Nguyen M.D.T., Yang S., Kim D. Pendant dual sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) proton exchange membranes for fuel cell application. J. Power Sources. 2016;328:355–363. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.041. - DOI
-
- Iojoiu C., Chabert F., Maréchal M., Kissi N., Guindet J., Sanchez J.Y. From polymer chemistry to membrane elaboration. J. Power Sources. 2006;153:198–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.05.039. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

