Microglia Purinoceptor P2Y6: An Emerging Therapeutic Target in CNS Diseases
- PMID: 32630251
- PMCID: PMC7407337
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9071595
Microglia Purinoceptor P2Y6: An Emerging Therapeutic Target in CNS Diseases
Abstract
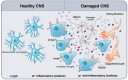
The purinergic receptor P2Y6 is expressed in immune cells, including the microglia that are implicated in neurological disorders. Its ligand, UDP, is a signaling molecule that can serve as an "find-me" signal when released in significant quantities by damaged/dying cells. The binding of UDP by P2Y6R leads to the activation of different biochemical pathways, depending on the disease context and the pathological environment. Generally, P2Y6R stimulates phagocytosis. However, whether or not phagocytosis coincides with cell activation or the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines needs further investigation. The current review aims to discuss the various functions of P2Y6R in some CNS disorders. We present evidence that P2Y6R may have a detrimental or beneficial role in the nervous system, in the context of neurological pathologies, such as ischemic stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, radiation-induced brain injury, and neuropathic pain.
Keywords: P2Y6R; microglia; neuroinflammation; phagocytosis; pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the review.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

