Immunoglobulin M Paraproteinaemias
- PMID: 32630470
- PMCID: PMC7352433
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12061688
Immunoglobulin M Paraproteinaemias
Abstract
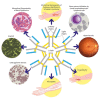
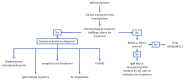
Monoclonal paraproteinaemia is an increasingly common reason for referral to haematology services. Paraproteinaemias may be associated with life-threatening haematologic malignancies but can also be an incidental finding requiring only observation. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) paraproteinaemias comprise 15-20% of monoclonal proteins but pose unique clinical challenges. IgM paraproteins are more commonly associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma than multiple myeloma and can occur in a variety of other mature B-cell neoplasms. The large molecular weight of the IgM multimer leads to a spectrum of clinical manifestations more commonly seen with IgM paraproteins than others. The differential diagnosis of B-cell and plasma cell dyscrasias associated with IgM gammopathies can be challenging. Although the discovery of MYD88 L265P and other mutations has shed light on the molecular biology of IgM paraproteinaemias, clinical and histopathologic findings still play a vital role in the diagnostic process. IgM secreting clones are also associated with a number of "monoclonal gammopathy of clinical significance" entities. These disorders pose a novel challenge from both a diagnostic and therapeutic perspective. In this review we provide a clinical overview of IgM paraproteinaemias while discussing the key advances which may affect how we manage these patients in the future.
Keywords: Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia; immunoglobulin M; lymphoma; multiple myeloma; paraproteinaemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kyle R.A., Durie B.G.M., Rajkumar S.V., Landgren O., Blade J., Merlini G., Kröger N., Einsele H., Vesole D.H., On Behalf of the International Myeloma Working Group et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma: IMWG consensus perspectives risk factors for progression and guidelines for monitoring and management. Leukemia. 2010;24:1121–1127. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.60. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

