The English (H6R) Mutation of the Alzheimer's Disease Amyloid-β Peptide Modulates Its Zinc-Induced Aggregation
- PMID: 32630528
- PMCID: PMC7355780
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10060961
The English (H6R) Mutation of the Alzheimer's Disease Amyloid-β Peptide Modulates Its Zinc-Induced Aggregation
Abstract
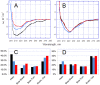
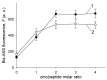
The coordination of zinc ions by histidine residues of amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ) plays a critical role in the zinc-induced Aβ aggregation implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. The histidine to arginine substitution at position 6 of the Aβ sequence (H6R, English mutation) leads to an early onset of AD. Herein, we studied the effects of zinc ions on the aggregation of the Aβ42 peptide and its isoform carrying the H6R mutation (H6R-Aβ42) by circular dichroism spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering, turbidimetric and sedimentation methods, and bis-ANS and thioflavin T fluorescence assays. Zinc ions triggered the occurrence of amorphous aggregates for both Aβ42 and H6R-Aβ42 peptides but with distinct optical properties. The structural difference of the formed Aβ42 and H6R-Aβ42 zinc-induced amorphous aggregates was also supported by the results of the bis-ANS assay. Moreover, while the Aβ42 peptide demonstrated an increase in the random coil and β-sheet content upon complexing with zinc ions, the H6R-Aβ42 peptide showed no appreciable structural changes under the same conditions. These observations were ascribed to the impact of H6R mutation on a mode of zinc/peptide binding. The presented findings further advance the understanding of the pathological role of the H6R mutation and the role of H6 residue in the zinc-induced Aβ aggregation.
Keywords: English mutation; aggregation; amyloid-β; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

