Special Low Protein Foods in the UK: An Examination of Their Macronutrient Composition in Comparison to Regular Foods
- PMID: 32630585
- PMCID: PMC7353443
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12061893
Special Low Protein Foods in the UK: An Examination of Their Macronutrient Composition in Comparison to Regular Foods
Abstract
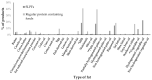
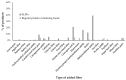
Special low protein foods (SLPFs) are essential in a low phenylalanine diet for treating phenylketonuria (PKU). With little known about their nutritional composition, all SLPFs on UK prescription were studied (n = 146) and compared to equivalent protein-containing foods (n = 190). SLPF nutritional analysis was obtained from suppliers/manufacturers. Comparable information about regular protein-containing foods was obtained from online UK supermarkets. Similar foods were grouped together, with mean nutritional values calculated for each subgroup (n = 40) and percentage differences determined between SLPFs and regular food subgroups. All SLPF subgroups contained 43-100% less protein than regular foods. Sixty-three percent (n = 25/40) of SLPF subgroups contained less total fat with palm oil (25%, n = 36/146) and hydrogenated vegetable oil (23%, n = 33/146) key fat sources. Sixty-eight percent (n = 27/40) of SLPF subgroups contained more carbohydrate, with 72% (n = 105/146) containing added sugar. Key SLPF starch sources were maize/corn (72%; n = 105/146). Seventy-seven percent (n = 113/146) of SLPFs versus 18% (n = 34/190) of regular foods contained added fibre, predominantly hydrocolloids. Nine percent of SLPFs contained phenylalanine > 25 mg/100 g and sources of phenylalanine/protein in their ingredient lists. Stricter nutritional composition regulations for SLPFs are required, identifying maximum upper limits for macronutrients and phenylalanine, and fat and carbohydrate sources that are associated with healthy outcomes.
Keywords: UK; macronutrients; nutritional composition; phenylketonuria; special low protein foods.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. has been a member of the European Nutritionist Expert Panel Biomarin, Sapropterin Advisory Board Biomarin, the advisory board ELEMENT Danone-Nutricia, the advisory board for Arla and Applied Pharma Research, and received research funding and honoraria from Nutricia, Vitaflo International and Merck Serono. J.C.R. has been a member of the European Nutritionist Expert Panel (Biomarin), the Advisory Board for Applied Pharma Research and Nutricia, and received honoraria as a speaker from APR, Merck Serono, Biomarin, Nutricia, Vitaflo, Cambrooke, PIAM and Lifediet. S.E. receives research funding from Nutricia, and has received financial support and honoraria from Nutricia and Vitaflo to attend/speak at study days and conferences.
Figures

References
-
- Van Wegberg A.M.J., MacDonald A., Ahring K., Bélanger-Quintana A., Blau N., Bosch A.M., Burlina A., Campistol J., Feillet F., Giżewska M., et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. [(accessed on 20 May 2020)];Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017 12:162. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0685-2. Available online: https://ojrd.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13023-017-0685-2. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

