Zearalenone-Induced Interaction between PXR and Sp1 Increases Binding of Sp1 to a Promoter Site of the eNOS, Decreasing Its Transcription and NO Production in BAECs
- PMID: 32630586
- PMCID: PMC7354576
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12060421
Zearalenone-Induced Interaction between PXR and Sp1 Increases Binding of Sp1 to a Promoter Site of the eNOS, Decreasing Its Transcription and NO Production in BAECs
Abstract
Zearalenone (ZEN) is a non-steroidal mycotoxin that has various toxicological impacts on mammalian health. Here, we found that ZEN significantly affected the production of nitric oxide (NO) and the expression of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) of bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs). A promoter analysis using 5'-serially deleted human eNOS promoter revealed that the proximal region (-135 to +22) was responsible for ZEN-mediated reduction of the human eNOS promoter activity. This effect was reversed by mutation of two specificity protein 1 (Sp1) binding elements in the human eNOS promoter. A chromatin immunoprecipitation assay revealed that ZEN increased Sp1 binding to the bovine eNOS promoter region (-113 to -12), which is homologous to -135 to +22 of the human eNOS promoter region. We also found that ZEN promoted the binding of the pregnane X receptor (PXR) to Sp1 of the bovine eNOS, consequently decreasing eNOS expression. This reduction of eNOS could have contributed to the decreased acetylcholine-induced vessel relaxation upon ZEN treatment in our ex vivo study using mouse aortas. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that ZEN decreases eNOS expression by enhancing the binding of PXR-Sp1 to the eNOS promoter, thereby decreasing NO production and potentially causing vessel dysfunction.
Keywords: NO; PXR; Sp1; eNOS; zearalenone.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
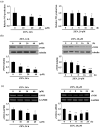

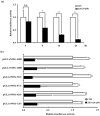


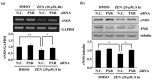
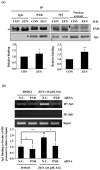
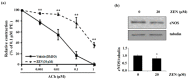
 ) are indicated in bold. (b) After pretreatment with vehicle or 20 nM of the Sp1 inhibitor mithramycin A for 1 h, BAECs were further co-treated with or without 20 μM of ZEN for 8 h. Binding of Sp1 to the bovine eNOS promoter gene relative to the total chromatin extract (Input) was quantified using a ChIP assay, as described in Materials and Methods. (c) Luciferase activities of the bovine eNOS(−135) vector and CMV promoter (Renilla) in BAECs treated with vehicle or 20 nM mithramycin A for 1 h, followed by further co-treatment with 20 µM of ZEN for 8 h. (d) Protein expression of eNOS relative to tubulin was quantified using Western blot analyses, and (e) NO production was quantified using the Griess method in BAECs treated with vehicle or 20 nM mithramycin A followed by further co-treatment with 20 µM ZEN for 4, 8, 16, and 24 h. (f) Protein expression of eNOS relative to tubulin was quantified using Western blot analyses of BAECs transfected with siRNA targeting Sp1 for 24 h and then exposed to 20 µM of ZEN for 8 h. N.C., negative control. Plots depict mean fold alterations from the control (± S.D.) from at least four independent trials. Statistical significance is denoted as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and N.S. (not statistically significant).
) are indicated in bold. (b) After pretreatment with vehicle or 20 nM of the Sp1 inhibitor mithramycin A for 1 h, BAECs were further co-treated with or without 20 μM of ZEN for 8 h. Binding of Sp1 to the bovine eNOS promoter gene relative to the total chromatin extract (Input) was quantified using a ChIP assay, as described in Materials and Methods. (c) Luciferase activities of the bovine eNOS(−135) vector and CMV promoter (Renilla) in BAECs treated with vehicle or 20 nM mithramycin A for 1 h, followed by further co-treatment with 20 µM of ZEN for 8 h. (d) Protein expression of eNOS relative to tubulin was quantified using Western blot analyses, and (e) NO production was quantified using the Griess method in BAECs treated with vehicle or 20 nM mithramycin A followed by further co-treatment with 20 µM ZEN for 4, 8, 16, and 24 h. (f) Protein expression of eNOS relative to tubulin was quantified using Western blot analyses of BAECs transfected with siRNA targeting Sp1 for 24 h and then exposed to 20 µM of ZEN for 8 h. N.C., negative control. Plots depict mean fold alterations from the control (± S.D.) from at least four independent trials. Statistical significance is denoted as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and N.S. (not statistically significant).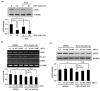
References
-
- Zatecka E., Ded L., Elzeinova F., Kubatova A., Dorosh A., Margaryan H., Dostalova P., Korenkova V., Hoskova K., Peknicova J. Effect of zearalenone on reproductive parameters and expression of selected testicular genes in mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014;45:20–30. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

