Figure 4
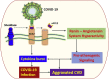
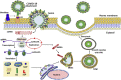
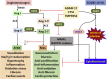
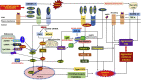
Proposed molecular mechanism underlying aggravated inflammatory response in COVID-19–CVD comorbidity. The components of COVID-19, including the RNA and proteins, act as intracellular PAMPs, which are recognized by conventional pattern recognition receptors, especially TLRs, RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), and NLRP3 inflammasome. The TLRs, including TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9, detect viral genome in the endosomal vesicles. In addition, the viral genome in the cytosol are recognized by the cytosolic receptors including RIG-1 and MDA5. The binding of viral ligands with the receptors initiates the recruitment and assembly of adaptor proteins including TRIF, MAVS, and STING, which trigger the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB and IRF3 via MyD88 adapter. IRF3 triggers the expression of type I IFNs, whereas NF-κB stimulates the expression of a battery of proinflammatory cytokines leading to cytokine burst. IL-1β is generated by the proteolytic activation of pro–IL-1β by caspase-1 following the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. The active NLRP3 inflammasome upregulates the transcription of pro–IL-1β gene and subsequent activation by caspase-1. The COVID-19 proteins including MP, SEP, and ORF3a activate NLRP3 via TRAF3 and subsequent IL-1β and ORF3a activate NF-κB and downstream cytokine burst. The apoptotic/necrotic cells following virus infection upregulate ADAM-17, the major sheddase for ACE2. IL-1β and TNF-α enhance the ACE2 shedding. The resultant sACE2 is a potent mediator for vascular inflammation and CVD pathology. ADAM-17 activates atherosclerotic plaque rupture and vascular inflammation. ACE2 inhibits the DAMPs, including HMGB1 released from the infected and ischemic/necrotic cells due to membrane damage. The decreased levels of ACE2 lead to increased DAMPs, especially OxLDL, HMGB1, AGEs, and ROS. These mediators trigger NLRP3 inflammasome via TLR2, TLR4, RAGE, and/or TREM1 axes in cardiovascular system. The upregulation of such DAMPs in the ACE2-depleted environment is detrimental, resulting in aggravated COVID-19–CVD comorbidity. ADAM-17, ADAM metallopeptidase domain-17; OxLDL, oxidized low-density lipoprotein; AGEs, advanced glycation end products; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; TLR, Toll-like receptor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein including IFN-β; RIG-1, retinoic acid-inducible gene 1; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; STING, stimulator of interferon genes protein; MP, matrix protein; MAV, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; TRAF3, TNF receptor-associated factor; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; ORF, open reading frame; SEP, small envelope protein; NLRP3, Nod-like receptor protein 3; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; CVD, cardiovascular disease.