Incubation period of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Busan, South Korea
- PMID: 32631735
- PMCID: PMC7311919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.06.018
Incubation period of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Busan, South Korea
Abstract
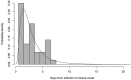
The assessment of the incubation period, which is the period between the infection and the illness onset, is essential to identify the sufficient isolation period for infectious diseases. In South Korea, a few cases of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) were identified after the 14-day self-quarantine program, and the length of this quarantine has raised controversial issues for the Korean public health professionals. We estimated the COVID-19 incubation period using the log-normal distribution from publicly available data. The data were obtained from the press release of the Busan city department of public health and news reports. We collected and analysed information for 47 patients with a median age of 30. We estimated that the median incubation period was three days (95% Confidence Interval, 0.6-8.2). We also did not find any significant difference in the incubation period between males and females. Our findings indicate that a 14-day self-quarantine program should be sufficient to prevent spreading in the infection of suspected individuals with COVID-19 in the community.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Incubation period; Korea; Log-normal distribution; Outbreak.
Copyright © 2020 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wonjin Cho. There is no addional cases identified in busan. Seoul, Korea: Sedaily. https://www.sedaily.com/NewsVIew/1Z04B9QJ8R [accessed 29 June 2020].
-
- Johan Giesecke. CRC Press; New York, NY: 2017. Modern infectious disease epidemiology.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources