Viral non-coding RNAs: Stealth strategies in the tug-of-war between humans and herpesviruses
- PMID: 32631785
- PMCID: PMC7779692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.015
Viral non-coding RNAs: Stealth strategies in the tug-of-war between humans and herpesviruses
Abstract
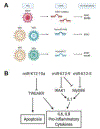
Oncogenic DNA viruses establish lifelong infections in humans, and they cause cancers, often in immunocompromised patients, despite anti-viral immune surveillance targeted against viral antigens. High-throughput sequencing techniques allowed the field to identify novel viral non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). ncRNAs are ideal factors for DNA viruses to exploit; they are non-immunogenic to T cells, thus viral ncRNAs can manipulate host cells without evoking adaptive immune responses. Viral ncRNAs may still trigger the host innate immune response, but many viruses encode decoys/inhibitors to counter-act and evade recognition. In addition, ncRNAs can be secreted to the extracellular space and influence adjacent cells to create a pro-viral microenvironment. In this review, we present recent progress in understanding interactions between oncoviruses and ncRNAs including small and long ncRNAs, microRNAs, and recently identified viral circular RNAs. In addition, potential clinical applications for ncRNA will be discussed. Extracellular ncRNAs are suggested to be diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and, with the realization of the importance of viral ncRNAs in tumorigenesis, approaches to target critical viral ncRNAs are emerging. Further understanding of viral utilization of ncRNAs will advance anti-viral therapeutics beyond conventional medication and vaccination.
Keywords: Circular RNA; Herpesvirus; Immune evasion; Non-coding RNA; Tumorigenesis; microRNA.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

