MapA, a Second Large RTX Adhesin Conserved across the Pseudomonads, Contributes to Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens
- PMID: 32631946
- PMCID: PMC7925077
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00277-20
MapA, a Second Large RTX Adhesin Conserved across the Pseudomonads, Contributes to Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens
Abstract
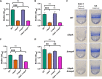
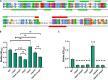
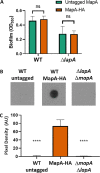
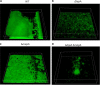
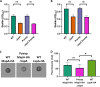
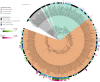
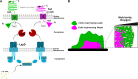
Mechanisms by which cells attach to a surface and form a biofilm are diverse and differ greatly among organisms. The Gram-negative gammaproteobacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens attaches to a surface through the localization of the large type 1-secreted RTX adhesin LapA to the outer surface of the cell. LapA localization to the cell surface is controlled by the activities of a periplasmic protease, LapG, and an inner membrane-spanning cyclic di-GMP-responsive effector protein, LapD. A previous study identified a second, LapA-like protein encoded in the P. fluorescens Pf0-1 genome: Pfl01_1463. Here, we identified specific growth conditions under which Pfl01_1463, here called MapA (
Keywords: Pseudomonas fluorescens; RTX; adhesin; biofilm; cyclic di-GMP.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

