Depression, obesity and their comorbidity during pregnancy: effects on the offspring's mental and physical health
- PMID: 32632208
- PMCID: PMC7850968
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-020-0813-6
Depression, obesity and their comorbidity during pregnancy: effects on the offspring's mental and physical health
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Depression, obesity and their comorbidity during pregnancy: effects on the offspring's mental and physical health.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Feb;26(2):482. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-01014-9. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33420482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
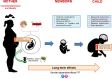
Depression and obesity represent two of the most common complications during pregnancy and are associated with severe health risks for both the mother and the child. Although several studies have analysed the individual effects of depression or obesity on the mothers and their children, the effects associated with the co-occurrence of both disorders have so far been poorly investigated. The relationship between depression and obesity is very complex and it is still unclear whether maternal depression leads to obesity or vice versa. It is well known that the intrauterine environment plays an important role in mediating the effects of both depression and obesity in the mother on the fetal programming, increasing the child's risk to develop negative outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
MAR has received compensation as speaker/consultant from Lundbeck, Otzuka, Recordati, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, and Sunovion, and he has received research grants from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and Sunovion, although none of these had a role in the preparation and publication of this article. All the other authors reported no financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sahrakorpi N, Koivusalo SB, Stach-Lempinen B, Eriksson JG, Kautiainen H, Roine RP. “The Burden of Pregnancy”; heavier for the heaviest? The changes in Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) assessed by the 15D instrument during pregnancy and postpartum in different body mass index groups: a longitudinal survey. Acta obstetricia et gynecologica Scandinavica. 2017;96:352–8. - PubMed
-
- Hasler G, Lissek S, Ajdacic V, Milos G, Gamma A, Eich D, et al. Major depression predicts an increase in long-term body weight variability in young adults. Obes Res. 2005;13:1991–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

