Risk, resilience, psychological distress, and anxiety at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany
- PMID: 32633464
- PMCID: PMC7361063
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1745
Risk, resilience, psychological distress, and anxiety at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany
Abstract
Background: The current COVID-19 pandemic comes with multiple psychological stressors due to health-related, social, economic, and individual consequences and may cause psychological distress. The aim of this study was to screen the population in Germany for negative impact on mental health in the current COVID-19 pandemic and to analyze possible risk and protective factors.
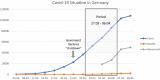
Methods: A total of 6,509 people took part in an online survey in Germany from 27 March to 6 April. The questionnaire included demographic information and ascertained psychological distress, anxiety and depressive symptoms, and risk and protective factors.
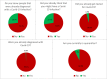
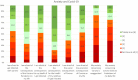
Results: In our sample, over 50% expressed suffering from anxiety and psychological distress regarding the COVID-19 pandemic. Participants spent several hours per day thinking about COVID-19 (M = 4.45). Psychological and social determinants showed stronger associations with anxiety regarding COVID-19 than experiences with the disease.
Conclusions: The current COVID-19 pandemic does cause psychological distress, anxiety, and depression for large proportions of the general population. Strategies such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and social contacts, acceptance of anxiety and negative emotions, fostering self-efficacy, and information on where to get medical treatment if needed, seem of help, while substance abuse and suppression of anxiety and negative emotions seem to be associated with more psychological burden.
Keywords: adjustment disorders; anxiety/anxiety disorders; coping; corona; depression.
© 2020 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bandura, A. (1988). Self‐efficacy conception of anxiety. Anxiety Research, 1(2), 77–98. 10.1080/10615808808248222 - DOI
-
- Bayrisches Staatsministerium für Gesundheit und Pflege (2020, January 27). Bestätigter Coronavirus‐Fall in Bayern – Infektionsschutzmaßnahmen laufen [Press release]. München.
-
- Beesdo‐Baum, K. , Klotsche, J. , Knappe, S. , Craske, M. G. , LeBeau, R. T. , Hoyer, J. , … Wittchen, H.‐U. (2012). Psychometric properties of the dimensional anxiety scales for DSM‐V in an unselected sample of German treatment seeking patients. Depression and Anxiety, 29(12), 1014–1024. 10.1002/da.21994 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bundesgesundheitsministerium (2020). Coronavirus SARS‐CoV‐2: Chronik der bisherigen Maßnahmen. Retrieved from www.bundesgesundheitsministerium.de/coronavirus/chronik-coronavirus.html.
-
- Bundesinstitut für Bevölkerungsforschung (2020). Durchschnittsalter der Bevölkerung (1871‐2018). Retrieved from https://www.bib.bund.de/DE/Fakten/Fakt/pdf/B19-Durchschnittsalter-Bevoel....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous