Medical innovations to maintain the function in patients with chronic PJI for whom explantation is not desirable: a pathophysiology-, multidisciplinary-, and experience-based approach
- PMID: 32633714
- PMCID: PMC7339926
- DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2020021
Medical innovations to maintain the function in patients with chronic PJI for whom explantation is not desirable: a pathophysiology-, multidisciplinary-, and experience-based approach
Abstract
Introduction: PJI is the most dramatic complication after joint arthroplasty. In patients with chronic infection, prosthesis exchange is in theory the rule. However, this surgical approach is sometimes not desirable especially in elderly patients with multiple comorbidities, as it could be associated with a dramatic loss of function, reduction of the bone stock, fracture, or peroperative death. We propose here to report different approaches that can help to maintain the function in such patients based on a pathophysiology-, multidisciplinary-, and an experience-based approach.
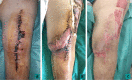
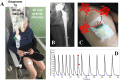
Methods: We describe the different points that are needed to treat such patients: (i) the multidisciplinary care management; (ii) understanding the mechanism of bacterial persistence; (iii) optimization of the conservative surgical approach; (iv) use of suppressive antimicrobial therapy (SAT); (v) implementation of innovative agents that could be used locally to target the biofilm.
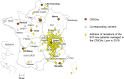
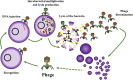
Results: In France, a nation-wide network called CRIOAc has been created and funded by the French Health ministry to manage complex bone and joint infection. Based on the understanding of the complex pathophysiology of PJI, it seems to be feasible to propose conservative surgical treatment such as "debridement antibiotics and implant retention" (with or without soft-tissue coverage) followed by SAT to control the disease progression. Finally, there is a rational for the use of particular agents that have the ability to target the bacteria embedded in biofilm such as bacteriophages and phage lysins.
Discussion: This multistep approach is probably a key determinant to propose innovative management in patients with complex PJI, to improve the outcome.
Conclusion: Conservative treatment has a high potential in patients with chronic PJI for whom explantation is not desirable. The next step will be to evaluate such practices in nation-wide clinical trials.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Bacteriophages; Innovations; Lysins; PJI; Phage therapy; Suppressive antimicrobial therapy.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2020.
Figures


References
-
- Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. (2013) Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 56, e1–e25. - PubMed
-
- Kapadia BH, Berg RA, Daley JA, et al. (2016) Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet 387, 386–394. - PubMed
-
- Société de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Française (SPILF), Collège des Universitaires de Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales (CMIT), Groupe de Pathologie Infectieuse Pédiatrique (GPIP), et al. (2010) Recommendations for bone and joint prosthetic device infections in clinical practice (prosthesis, implants, osteosynthesis). Société de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Française. Med Mal Infect 40, 185–211. - PubMed
-
- Ariza J, Cobo J, Baraia-Etxaburu J, et al. (2017) Executive summary of management of prosthetic joint infections. Clinical practice guidelines by the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC). Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 35, 189–195. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
