NC2 complex is a key factor for the activation of catalase-3 transcription by regulating H2A.Z deposition
- PMID: 32633757
- PMCID: PMC7470962
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa552
NC2 complex is a key factor for the activation of catalase-3 transcription by regulating H2A.Z deposition
Abstract
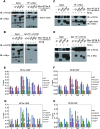
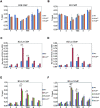
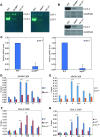
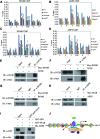
Negative cofactor 2 (NC2), including two subunits NC2α and NC2β, is a conserved positive/negative regulator of class II gene transcription in eukaryotes. It is known that NC2 functions by regulating the assembly of the transcription preinitiation complex. However, the exact role of NC2 in transcriptional regulation is still unclear. Here, we reveal that, in Neurospora crassa, NC2 activates catalase-3 (cat-3) gene transcription in the form of heterodimer mediated by histone fold (HF) domains of two subunits. Deletion of HF domain in either of two subunits disrupts the NC2α-NC2β interaction and the binding of intact NC2 heterodimer to cat-3 locus. Loss of NC2 dramatically increases histone variant H2A.Z deposition at cat-3 locus. Further studies show that NC2 recruits chromatin remodeling complex INO80C to remove H2A.Z from the nucleosomes around cat-3 locus, resulting in transcriptional activation of cat-3. Besides HF domains of two subunits, interestingly, C-terminal repression domain of NC2β is required not only for NC2 binding to cat-3 locus, but also for the recruitment of INO80C to cat-3 locus and removal of H2A.Z from the nucleosomes. Collectively, our findings reveal a novel mechanism of NC2 in transcription activation through recruiting INO80C to remove H2A.Z from special H2A.Z-containing nucleosomes.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone variant H2A.Z antagonizes the positive effect of the transcriptional activator CPC1 to regulate catalase-3 expression under normal and oxidative stress conditions.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Jun;121:136-148. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29738831
-
Chromatin remodeler Ino80C acts independently of H2A.Z to evict promoter nucleosomes and stimulate transcription of highly expressed genes in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 4;48(15):8408-8430. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa571. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32663283 Free PMC article.
-
HDA-2-Containing Complex Is Required for Activation of Catalase-3 Expression in Neurospora crassa.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0135122. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01351-22. Epub 2022 Jun 14. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35699373 Free PMC article.
-
Patterning chromatin: form and function for H2A.Z variant nucleosomes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Apr;16(2):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16503125 Review.
-
Contribution of the histone variant H2A.Z to expression of responsive genes in plants.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 15;135:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.006. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35474148 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A role for the mitotic proteins Bub3 and BuGZ in transcriptional regulation of catalase-3 expression.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jun 6;18(6):e1010254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010254. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35666721 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional kinetic synergy: A complex landscape revealed by integrating modeling and synthetic biology.Cell Syst. 2023 Apr 19;14(4):324-339.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2023.02.003. Cell Syst. 2023. PMID: 37080164 Free PMC article.
-
The nutrient-sensing GCN2 signaling pathway is essential for circadian clock function by regulating histone acetylation under amino acid starvation.Elife. 2023 Apr 21;12:e85241. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85241. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37083494 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor VIB-1 activates catalase-3 expression by promoting PIC assembly in Neurospora crassa.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 27;53(5):gkaf174. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40087884 Free PMC article.
-
SET-1-mediated H3K4me3 modification regulates catalase-3 expression in Neurospora crassa.Curr Genet. 2025 Aug 21;71(1):18. doi: 10.1007/s00294-025-01320-1. Curr Genet. 2025. PMID: 40839318
References
-
- Orphanides G., Lagrange T., Reinberg D.. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1996; 10:2657–2683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

