The value of genotypic and imaging information to predict functional and structural outcomes in ADPKD
- PMID: 32634120
- PMCID: PMC7455088
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.138724
The value of genotypic and imaging information to predict functional and structural outcomes in ADPKD
Abstract
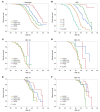
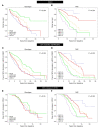
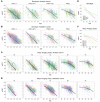
BACKGROUNDA treatment option for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) has highlighted the need to identify rapidly progressive patients. Kidney size/age and genotype have predictive power for renal outcomes, but their relative and additive value, plus associated trajectories of disease progression, are not well defined.METHODSThe value of genotypic and/or kidney imaging data (Mayo Imaging Class; MIC) to predict the time to functional (end-stage kidney disease [ESKD] or decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]) or structural (increase in height-adjusted total kidney volume [htTKV]) outcomes were evaluated in a Mayo Clinic PKD1/PKD2 population, and eGFR and htTKV trajectories from 20-65 years of age were modeled and independently validated in similarly defined CRISP and HALT PKD patients.RESULTSBoth genotypic and imaging groups strongly predicted ESKD and eGFR endpoints, with genotype improving the imaging predictions and vice versa; a multivariate model had strong discriminatory power (C-index = 0.845). However, imaging but not genotypic groups predicted htTKV growth, although more severe genotypic and imaging groups had larger kidneys at a young age. The trajectory of eGFR decline was linear from baseline in the most severe genotypic and imaging groups, but it was curvilinear in milder groups. Imaging class trajectories differentiated htTKV growth rates; severe classes had rapid early growth and large kidneys, but growth later slowed.CONCLUSIONThe value of imaging, genotypic, and combined data to identify rapidly progressive patients was demonstrated, and reference values for clinical trials were provided. Our data indicate that differences in kidney growth rates before adulthood significantly define patients with severe disease.FUNDINGNIDDK grants: Mayo DK058816 and DK090728; CRISP DK056943, DK056956, DK056957, and DK056961; and HALT PKD DK062410, DK062408, DK062402, DK082230, DK062411, and DK062401.
Keywords: Genetic diseases; Genetics; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
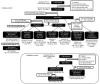
References
-
- [No authors listed]. United States Renal Data System, 2018 USDRS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. United States Renal Data System. https://www.usrds.org/2018/view/Default.aspx Accessed July 7, 2020.
-
- [No authors listed] The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Cell. 1994;78(4):725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK062401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062411/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062410/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113111/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025752/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR023940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062408/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM130423/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK126126/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001102/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

