The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Associated Belgian Governmental Measures on Cancer Screening, Surgical Pathology and Cytopathology
- PMID: 32634799
- PMCID: PMC7445376
- DOI: 10.1159/000509546
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Associated Belgian Governmental Measures on Cancer Screening, Surgical Pathology and Cytopathology
Abstract
Introduction: The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 caused a pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Unprecedented public health actions were introduced, including social distancing, travel restrictions and quarantine. The Belgian government announced a national emergency plan, thereby postponing all non-urgent medical consultations and operations. This report analyses the impact of these measures on cancer screening, through assessment of the workload of a laboratory for histopathology and cytopathology.
Methods: Data on monthly numbers of histological and cytological samples, immunohistochemistry and molecular tests were extracted from the laboratory information management system.
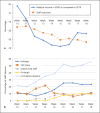
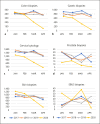
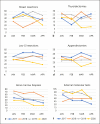
Results: The global histopathological and cytological workload was substantially reduced. The impact on oncology-related surgical procedures was rather limited. The anti-COVID-19 measures significantly diminished all screening-related samples, such as colon biopsies, breast biopsies and cervical cytology, and strongly reduced the number of samples related to "functional" pathology, such as thyroidectomies and gastric biopsies.
Conclusions: Since many health care interventions are reflected in the workload of a pathology laboratory, this study enabled us to identify areas for "deconfinement" health care actions. Our findings indicate that various areas in medicine were affected, but the impact seemed largest for cancer screening. Health care professionals should assure that consultations related to cancer screening are postponed instead of cancelled.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cancer screening; Cervical cytology; Histopathology; SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© 2020 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Investigations of Pathologists as a Key to Understanding Coronavirus Disease 2019.Pathobiology. 2021;88(1):11-14. doi: 10.1159/000513602. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Pathobiology. 2021. PMID: 33341799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Carinci F. Covid-19: preparedness, decentralisation, and the hunt for patient zero. BMJ. 2020 Feb;368:m799. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation Coronavirus disease. 2019. (COVID-19) - Situation report 51. www.who.int.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

